Neurangiosis designates inherently functional but different in origin and symptoms of vegetative disturbances. They are the consequences of neurohumoral regulation of the vegetative function. This disorder usually occurs during neuroses, hypodynamia, endocrine disharmonies during pubertal and climacteric periods, neurosis-like states caused by neuropsychic or physical overwork, infections, intoxications, abstinence (in case of toxicomania), etc.
The neurangiosis pathogenesis usually involves impaired regulation of vegetative activity at all levels, from the brain cortex to the peripheral segments of the vegetative nervous system (including adrenal and cholinoreceptors of the executive organs) and endocrine regulation segments.
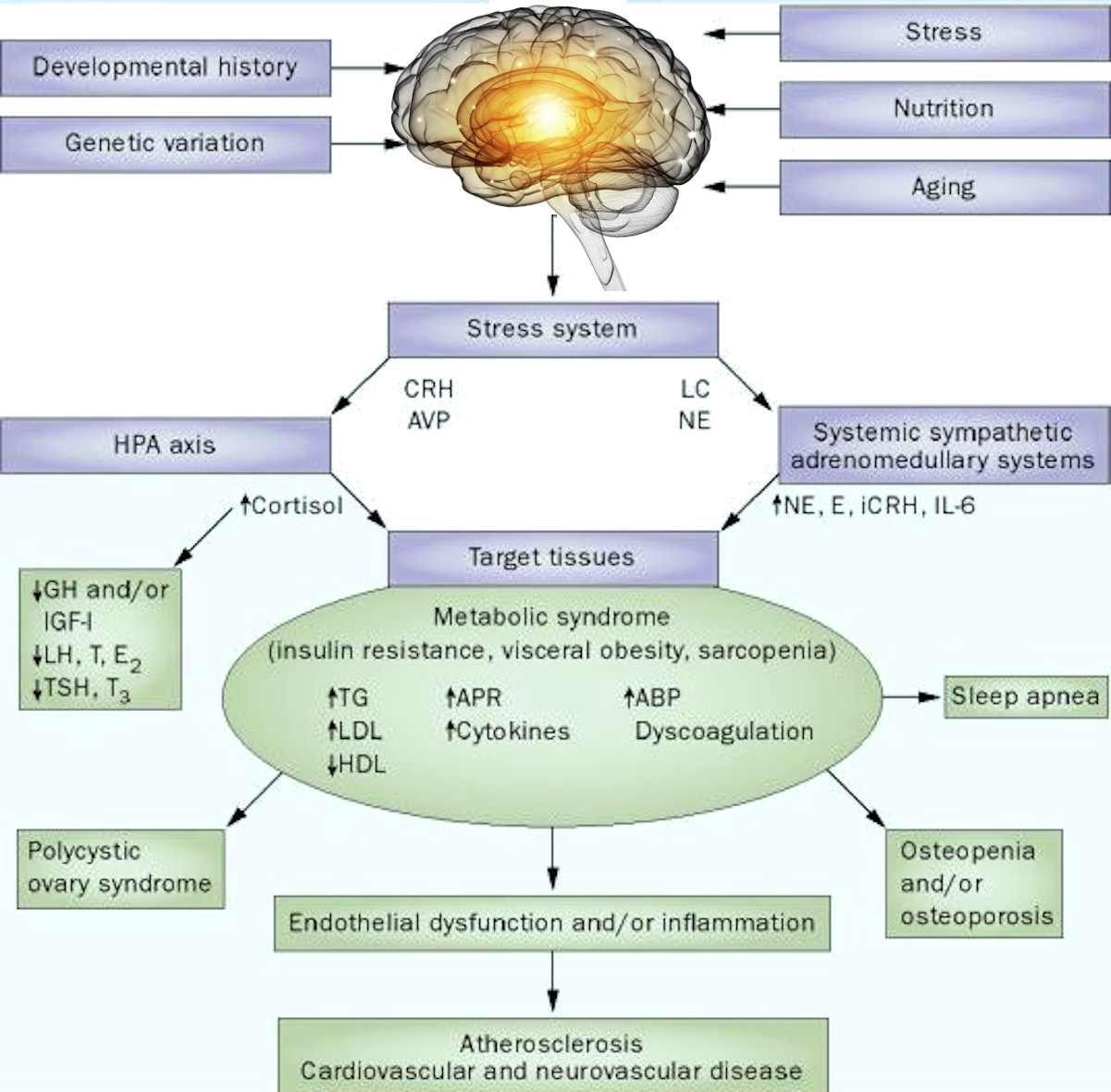
Neurohumoral regulation of the vegetative function
However, depending on the neurangiosis form and aetiology, the principal pathogenetic value for any level – cortical, subthalamic, etc. – can be specified, with the prevailing activity of either the parasympathetic or sympathetic segment of the vegetative nervous system. Most patients experience some form of asthenia or other fatigue, as well as irritability, sleep disturbances, and a low pain sensitivity threshold, accompanied by various senesthopathias (a sensation of insufficient breathing, cardialgia, a burning sensation in other body parts, etc.).

Mini Detox PLUS – 3 colonics, minerals, herbal & probiotic implants
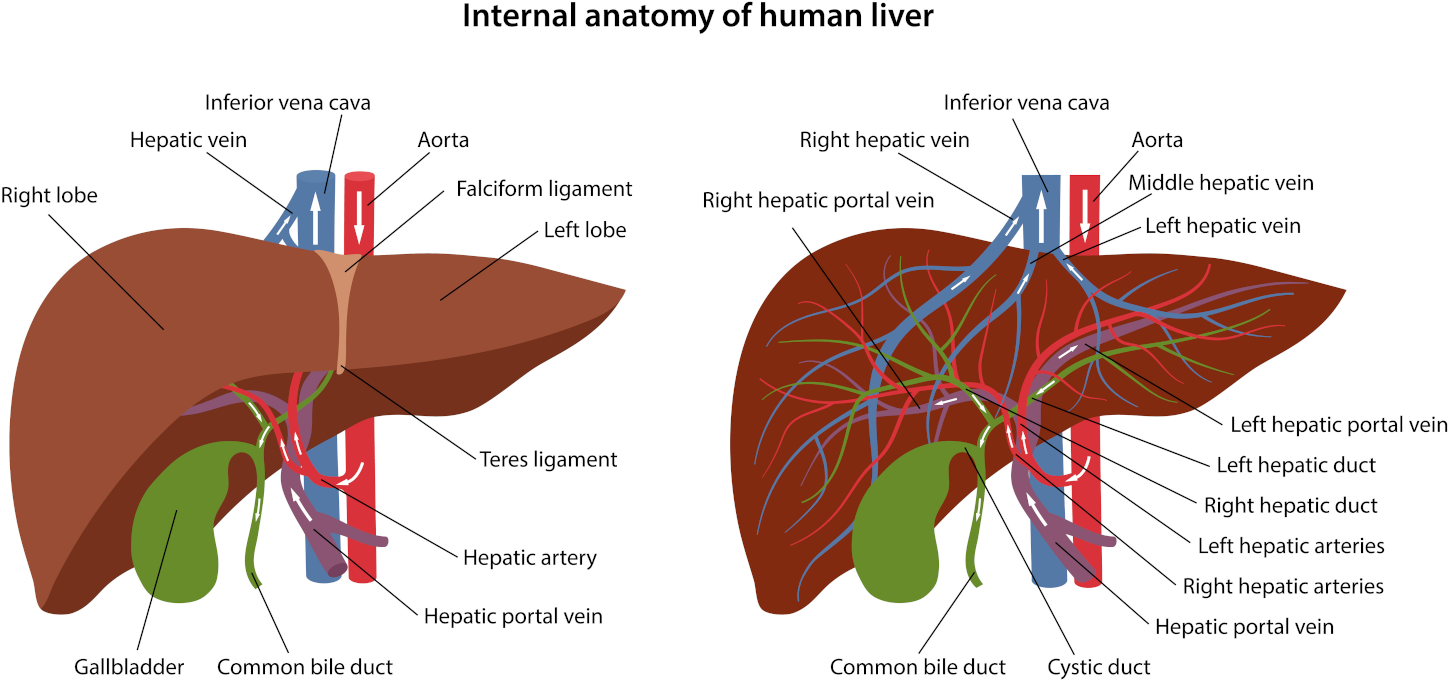
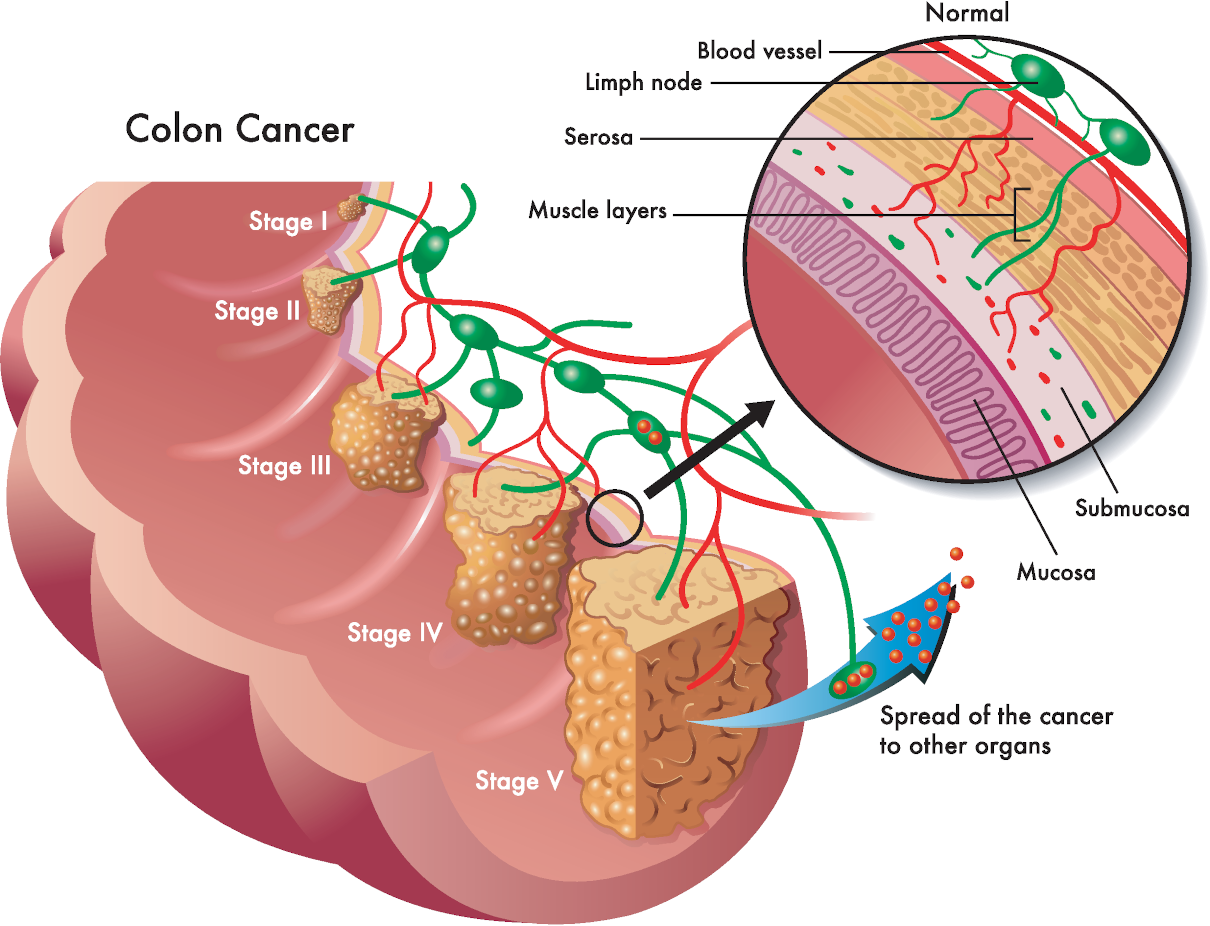
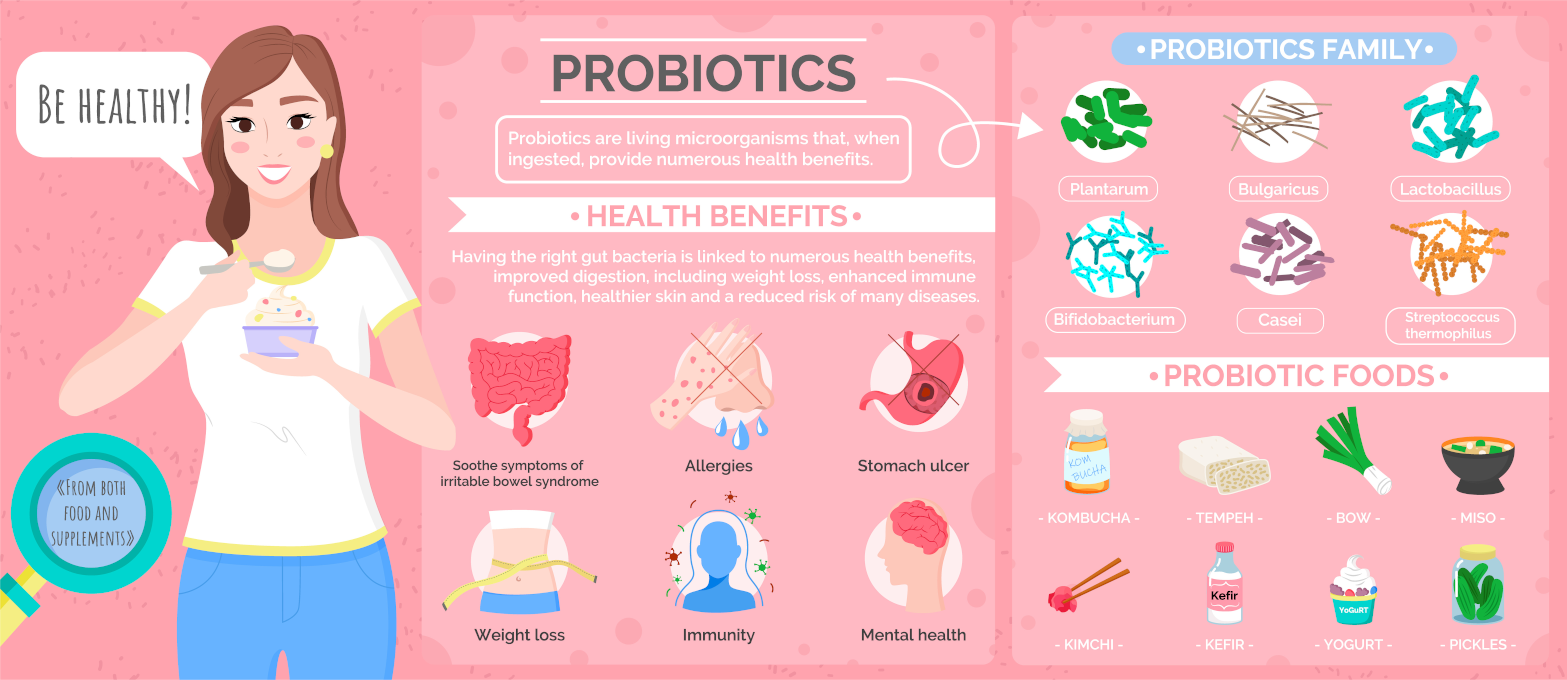
The ideal pattern of colonic treatments includes three alkalising colon hydrotherapy treatments with sodium bicarbonate, one anti-parasitic implant on the first treatment, one liver and gall bladder stimulating herbal implant on the second treatment, and a high-strength probiotic implant on the third colonic.
Among other vegetative dysfunctions, symptoms are
- a sensation of palpitation (in case of a predilection for sinus bradycardia or tachycardia),
- supraventricular (sometimes ventricular) extrasystolia,
- Bouveret’s disease,
- pathological vasomotor reactions – a sensation of fever and cold,
- arise or fall in arterial pressure,
- skin pallor or hyperemia,
- hand and foot chilliness,
- overall or mainly local (axillary, palmar) sweating,
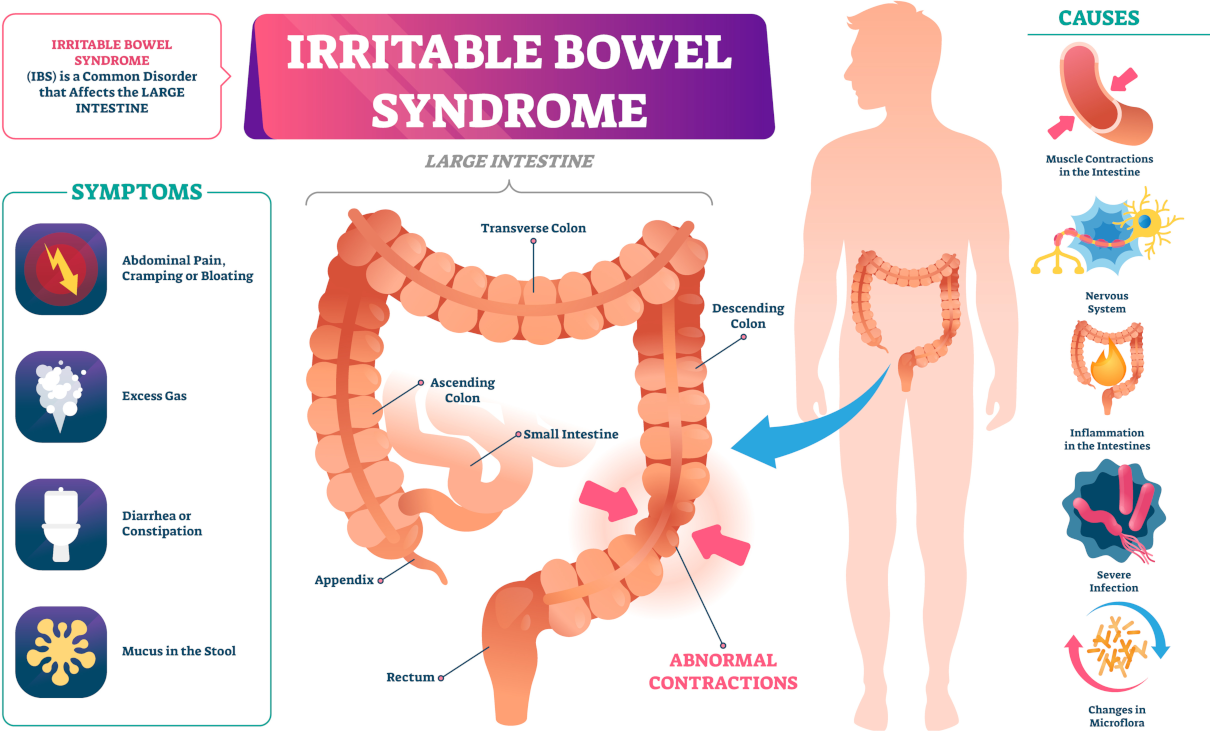
- secretory and motor gastrointestinal tract dysfunction,
- sexual function disturbances, etc.
In addition, we have accumulated significant statistics over the past fourteen years, providing preventive treatment to patients diagnosed with Neurangiosis. Additionally, we observed significant improvements in the overall health status of most patients undergoing regular colonic hydrotherapy with sodium bicarbonate. Moreover, positive effects are observed for longer with probiotic implants.
We also recommend a food intolerance test to minimise the number of factors negatively affecting health.