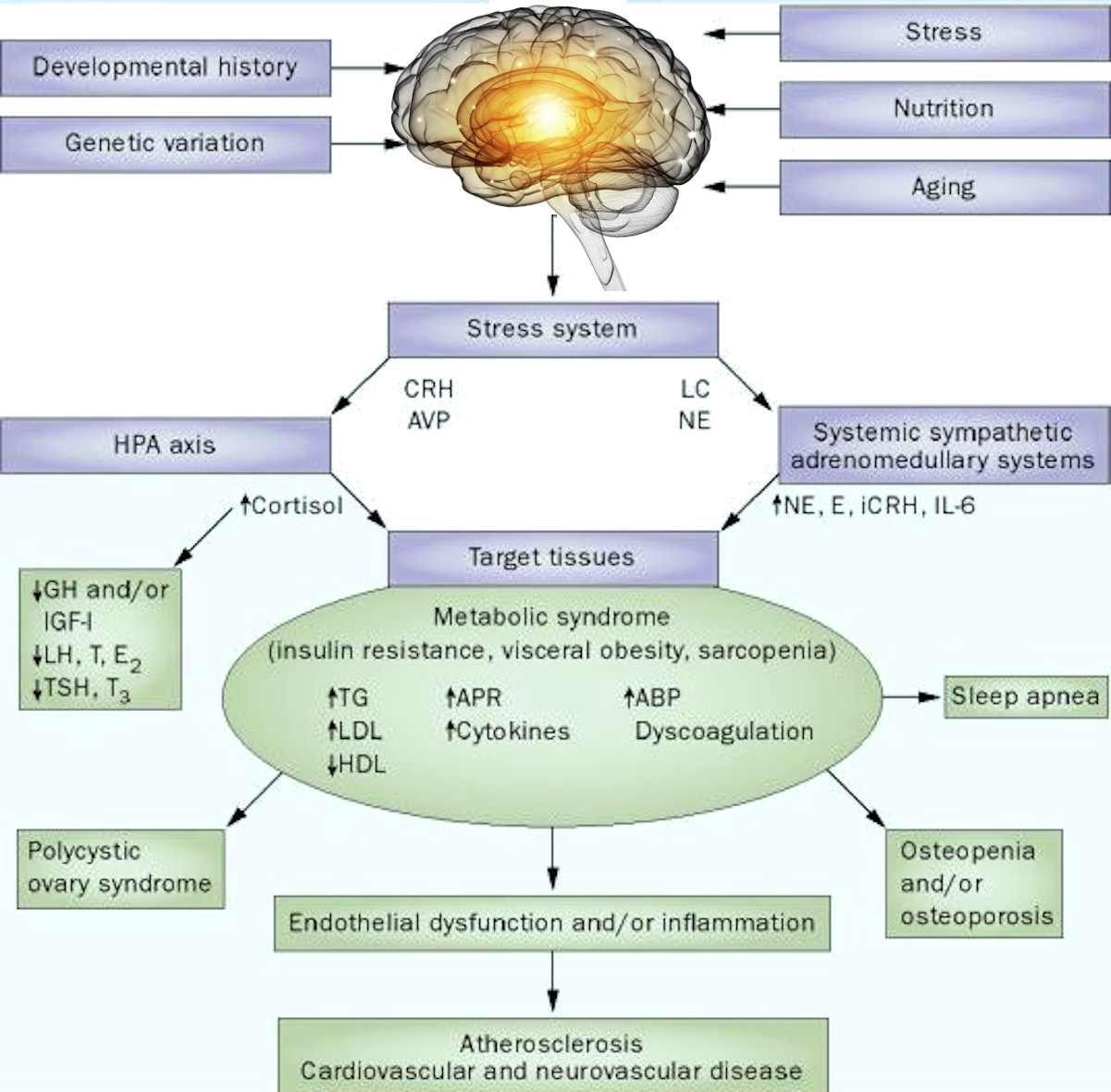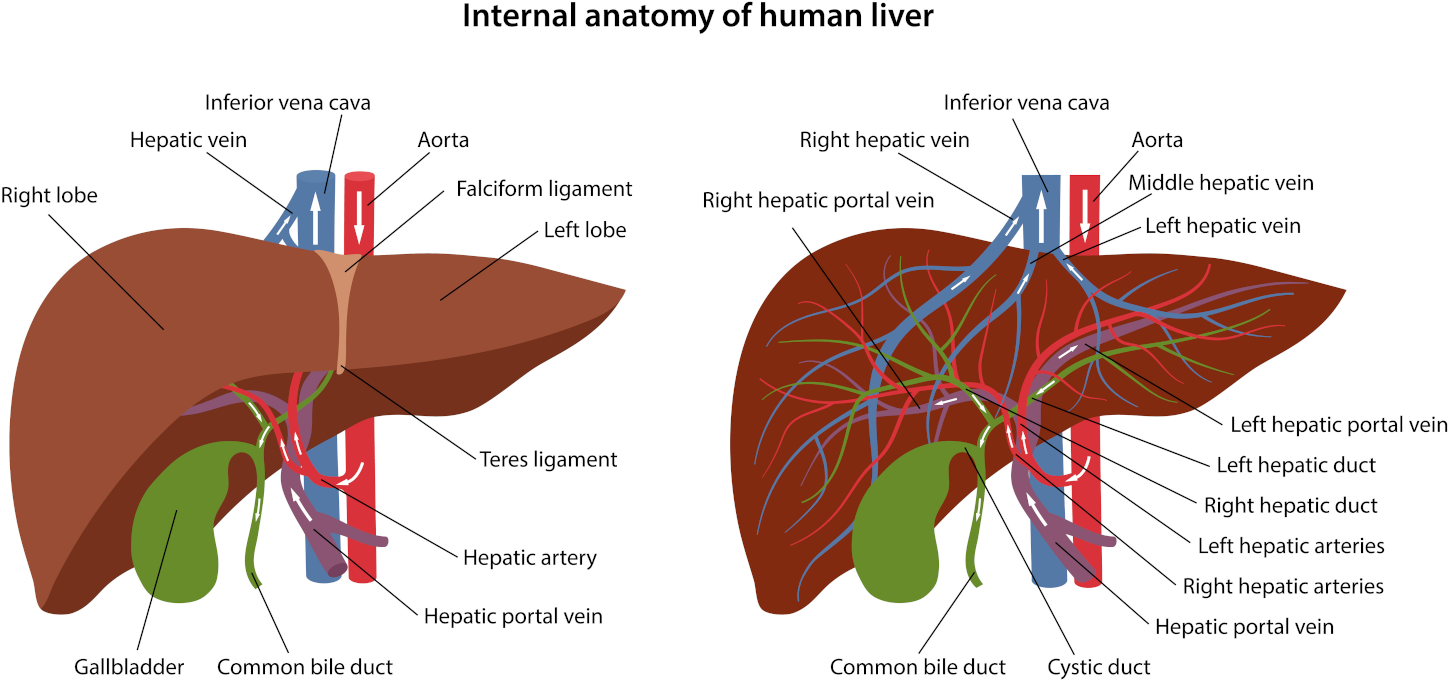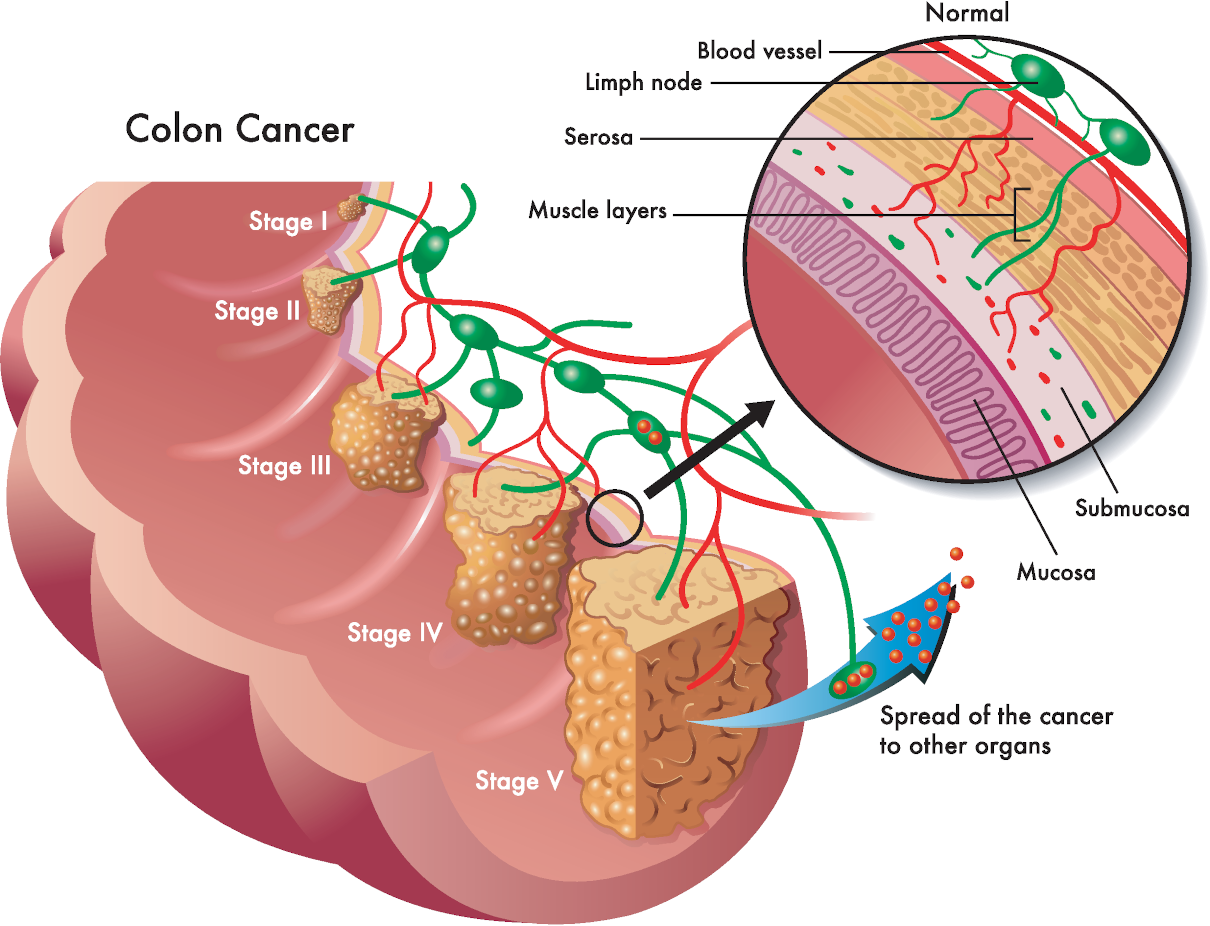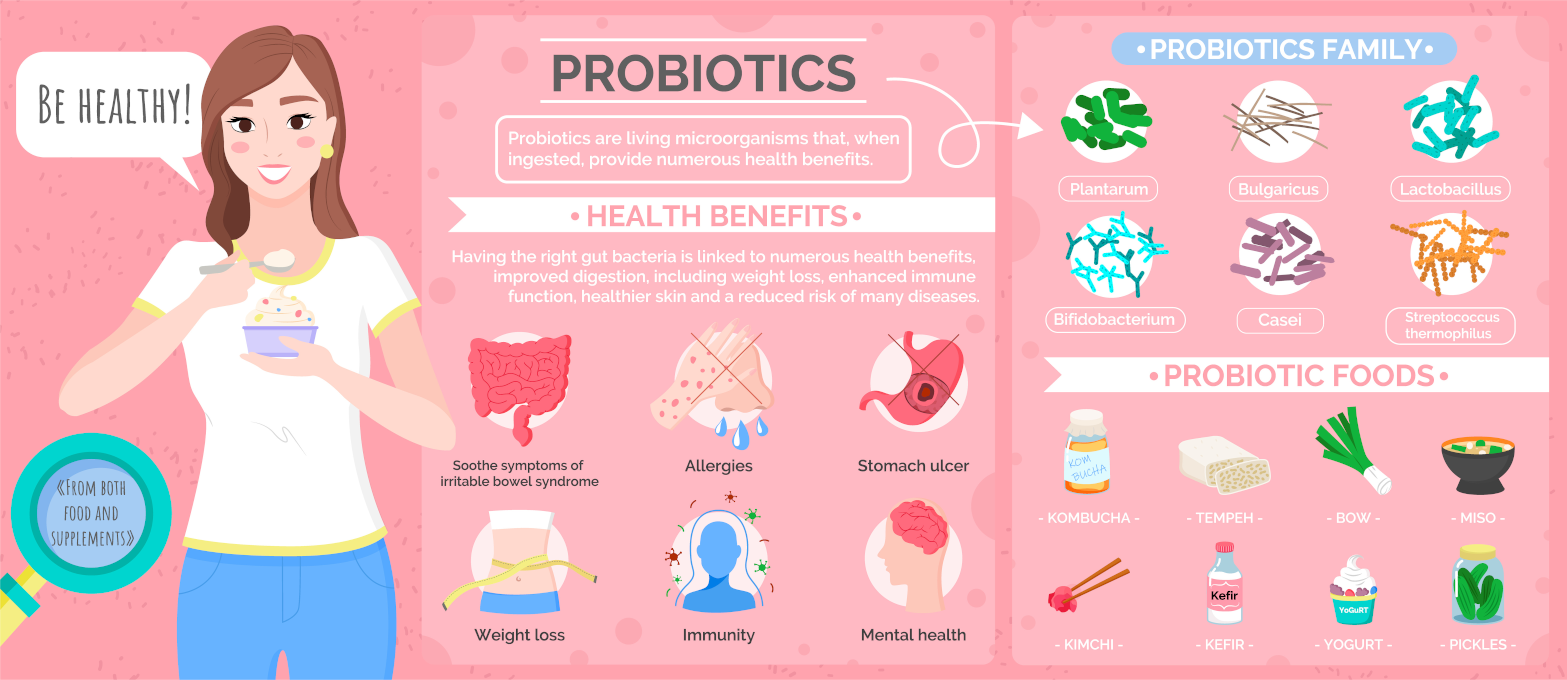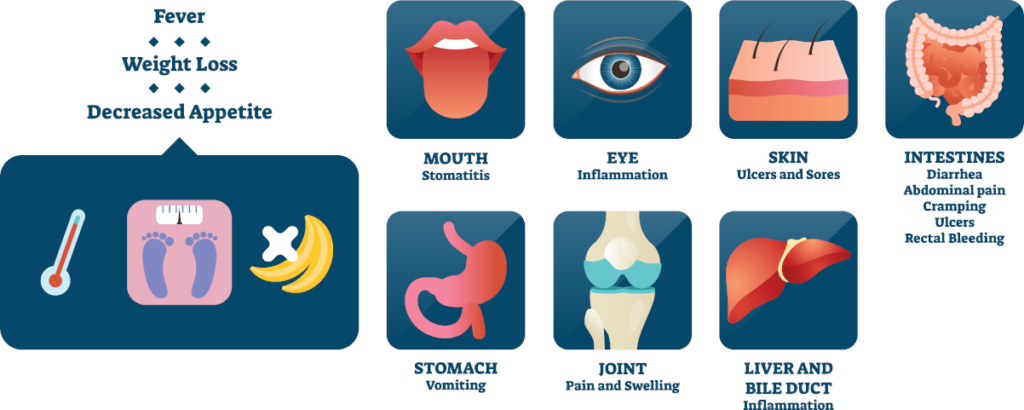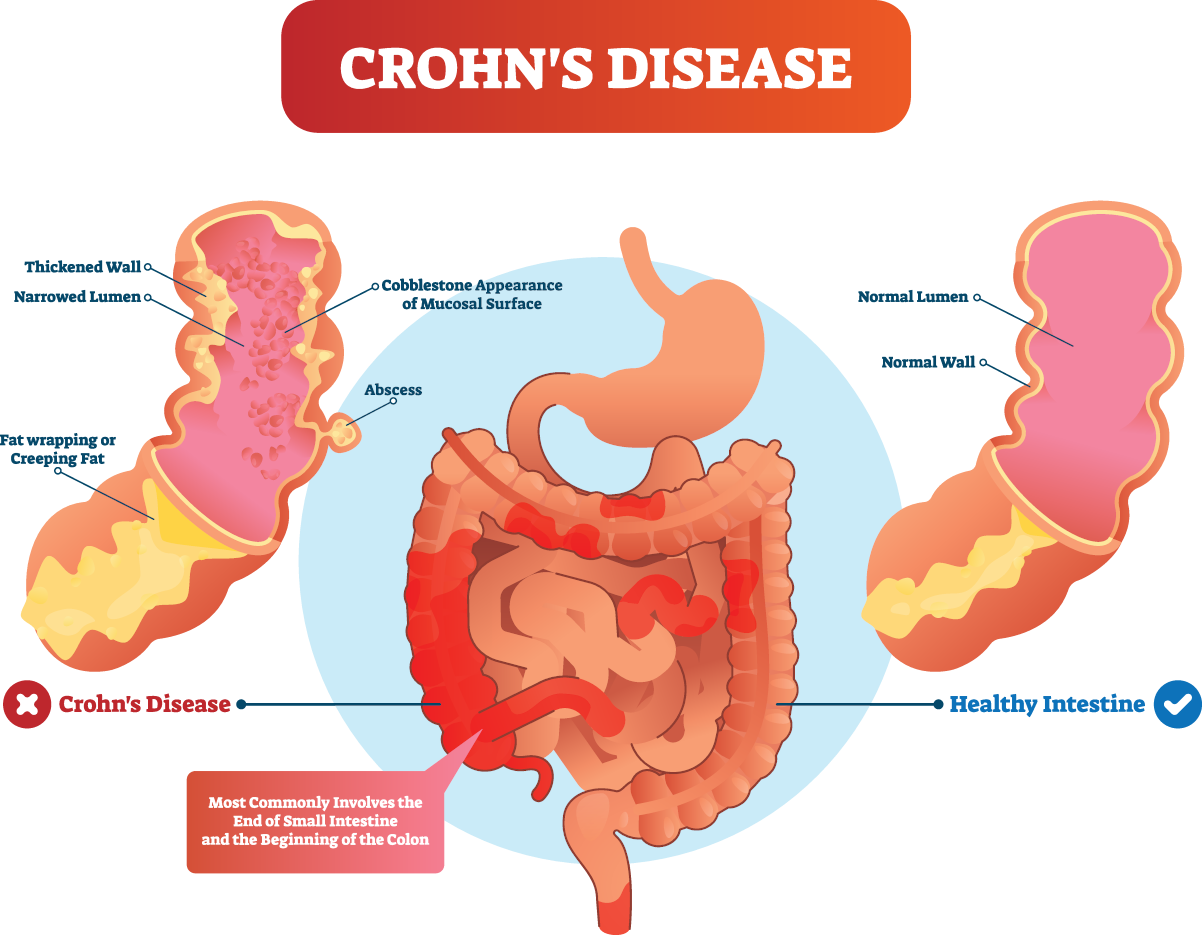
Crohn’s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn’s disease can affect any area of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most commonly affects the lower part of the small intestine, called the ileum. The swelling extends deep into the lining of the affected organ. The swelling can cause pain and make the intestines frequently empty, resulting in diarrhoea.
Pathology – Crohn’s disease
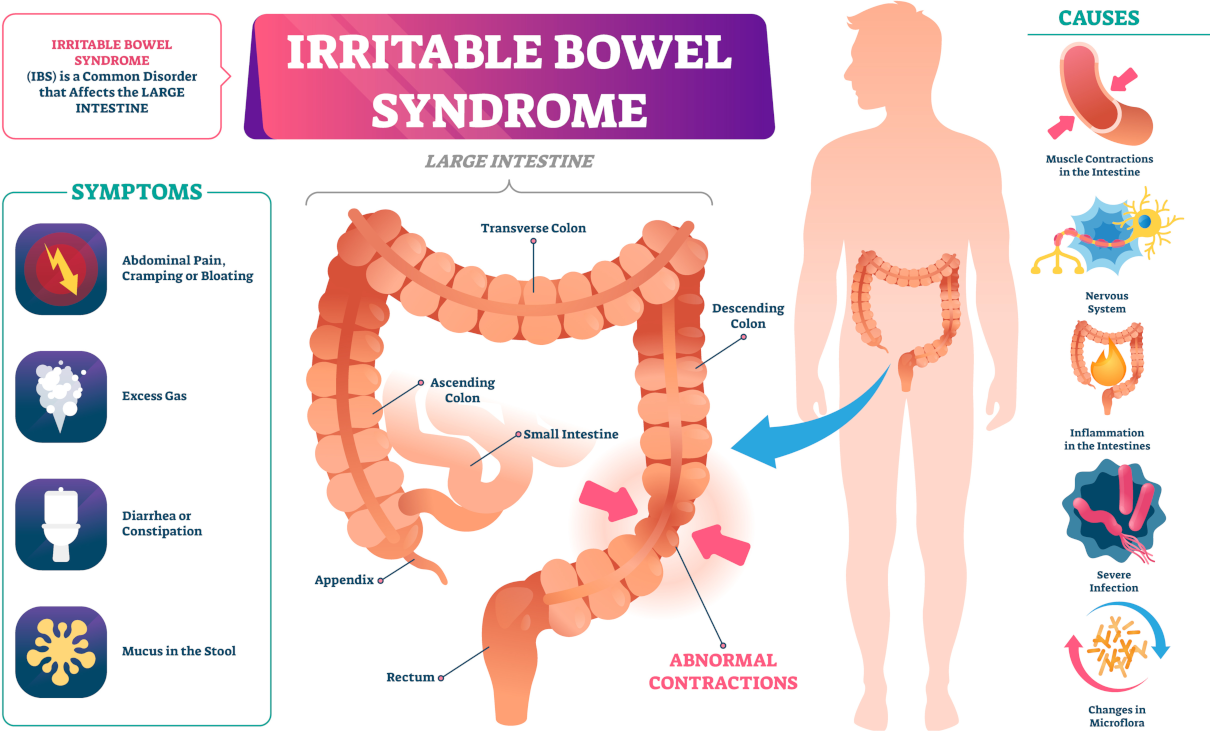
This pathology is an inflammatory bowel disease, the generic name for conditions that cause swelling in the intestines. The symptoms of disadvantage are similar to other intestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome and ulcerative colitis. It can also be challenging to diagnose.
Ulcerative colitis causes inflammation and ulcers in the top layer of the large intestine’s lining. All organ layers are involved in Crohn’s disease, and a normal, healthy bowel can be found between sections of the diseased bowel.
Currently, colonic treatments are available in our London clinic only

Colonic Irrigation with anti-spasmodic herbs & bicarbonate of soda
Colon cleansing with ENEMA HERBS & bicarbonate of soda is highly anti-spasmodic and helps void gas during colon hydrotherapy. It is especially beneficial in the presence of IBS and spasms. Your appointment will also include initial consultation.
Diagnostic
Pathology affects men and women equally and seems to run in some families. About 20 per cent of people with Crohn’s disease have a blood relative with some inflammatory bowel disease. Often, this is a brother or sister and sometimes a parent or child.
This pathology can occur in people of all age groups. However, medics more commonly diagnose it in people between 20 and 30. For instance, people from the Middle East have an increased risk of developing Crohn’s disease. However, African Americans are at decreasing risk of developing that condition.

Food intolerance test of 208 ingredients
This is our most comprehensive food and drink test. It analyses your client’s IgG antibody reactions to 208 food and drink ingredients. This test will highlight their food triggers and help you formulate an IgG-guided elimination diet together.