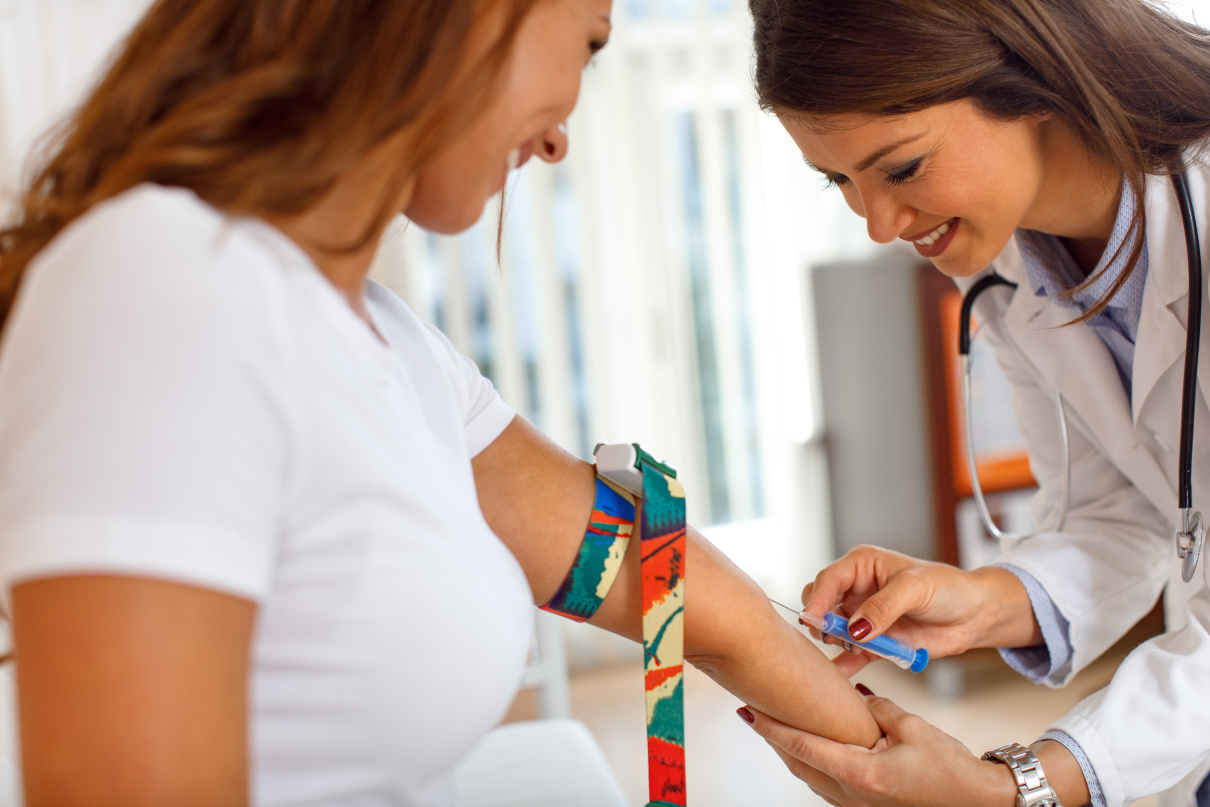
What is interferon for the immune system? The body’s immune system exists to fight against all matter of pathogens and foreign bodies, including cancer cells. It can mainly cope on its own when dealing with microbes and viruses. But worms and tumours are too uncontrollable for it, unfortunately.
The immune system consists of two parts: innate and acquired immunity. Scientists also categorise the latter as either passive or active.
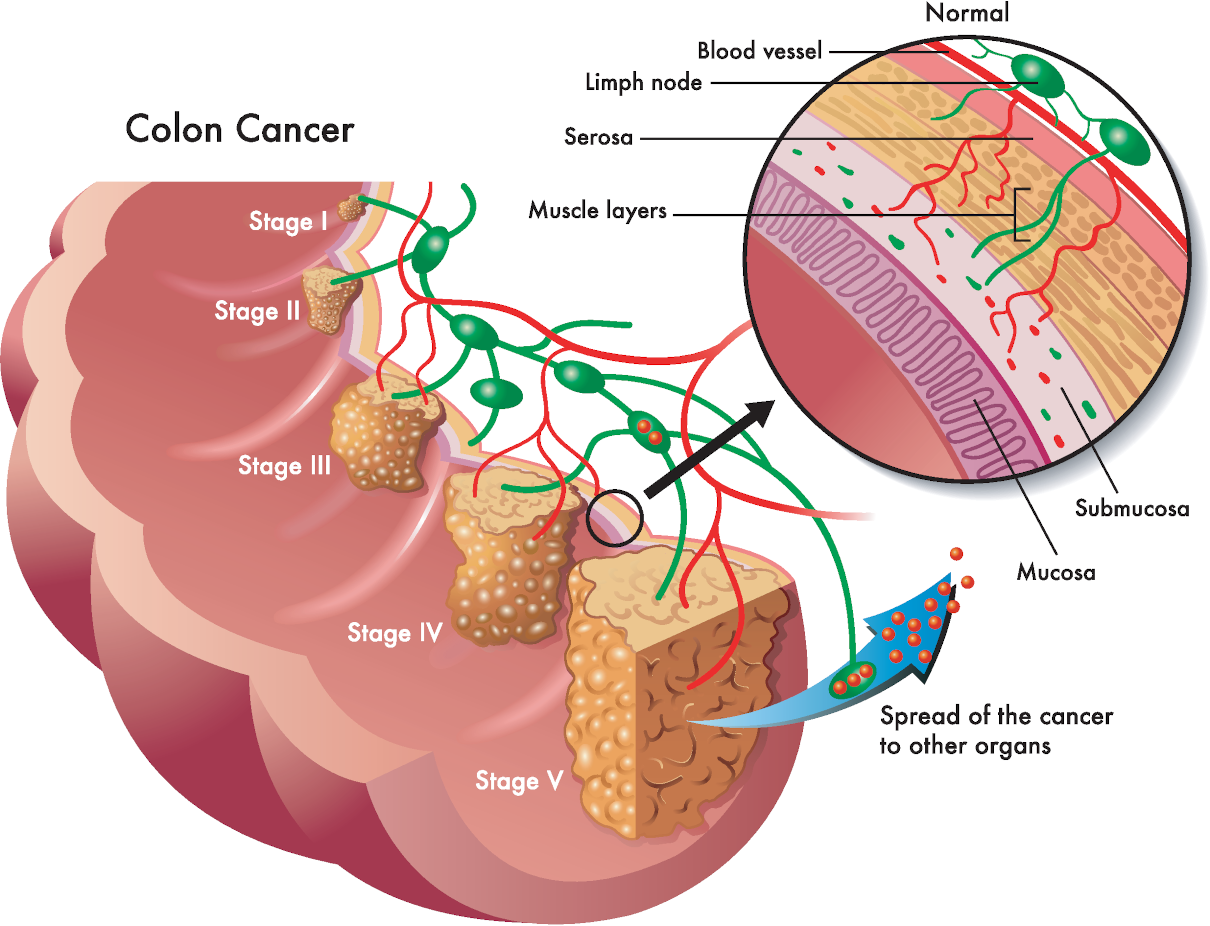
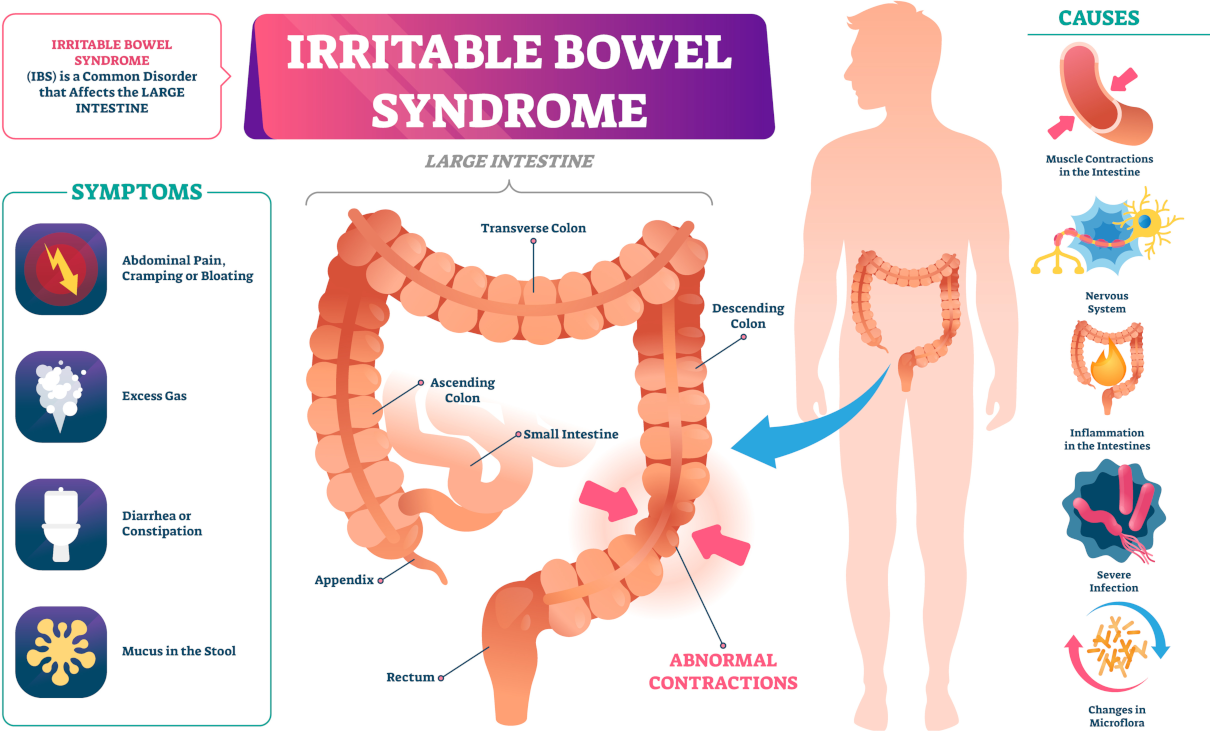
Symptoms of bowel cancer
White blood cells, leukocytes, lymphocytes, and platelets are responsible for the majority of the immune system’s work. The immune system also works through different body fluids, such as saliva, mucus of the stomach and intestines, and blood.
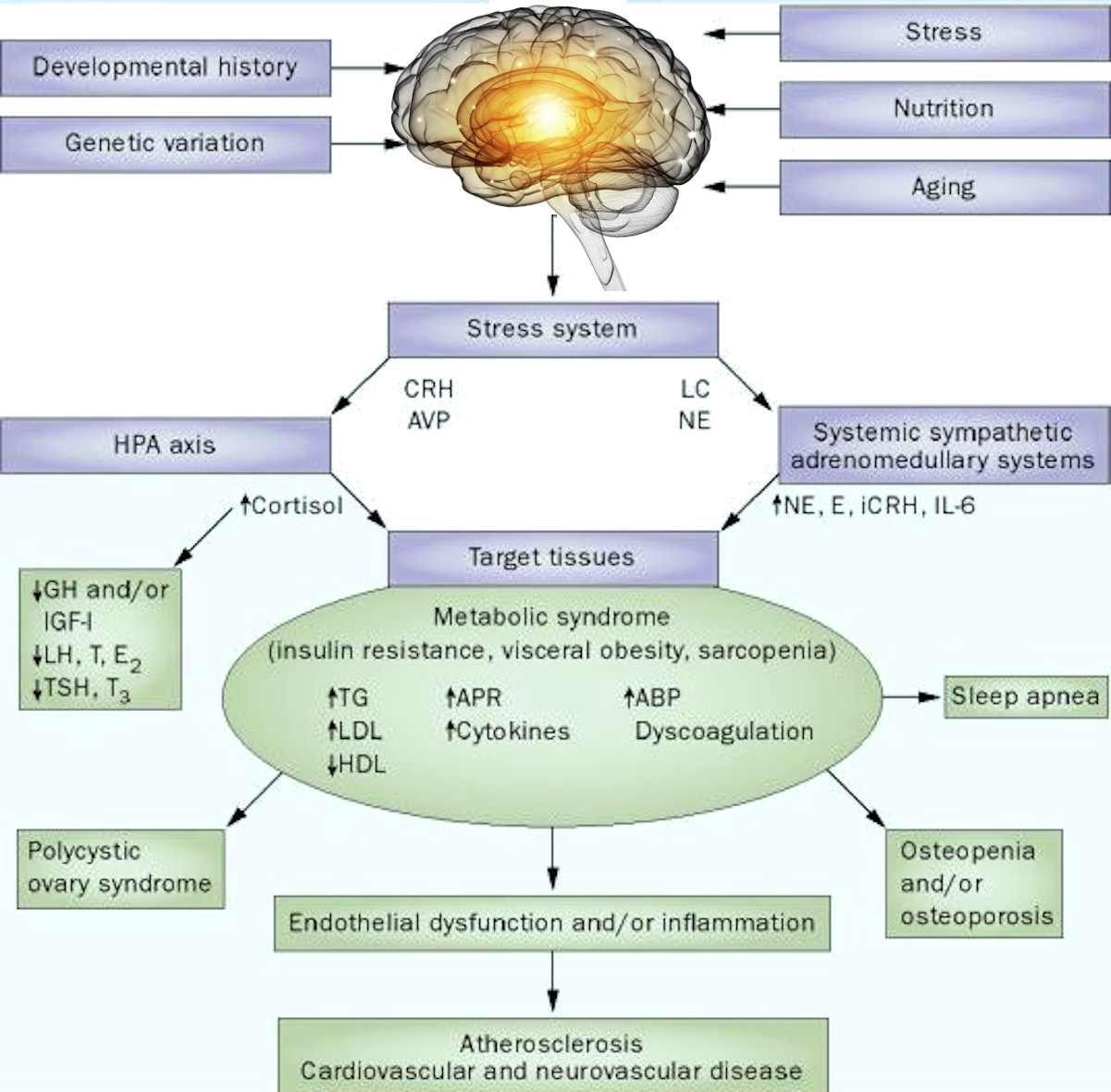
In particular, type I and II interferons (IFNs) are involved in many mechanisms that regulate immune responses in cancer, thus balancing immune escape versus immune surveillance.

One colonic irrigation session including consultation
Colon irrigation and comprehensive consultation with a professional colon hydrotherapist registered with RICTAT and ARCH at the Parkland Clinic in Holborn. We use a closed system only—London’s best colonic hydrotherapy deal.
Interferon and drugs based on it.
Interferon is a natural protein responsible for fighting infections in the human body.
Medics use interferon-based medications in modern clinical procedures worldwide to treat various infectious and viral diseases, including influenza and SARS.
Mechanism
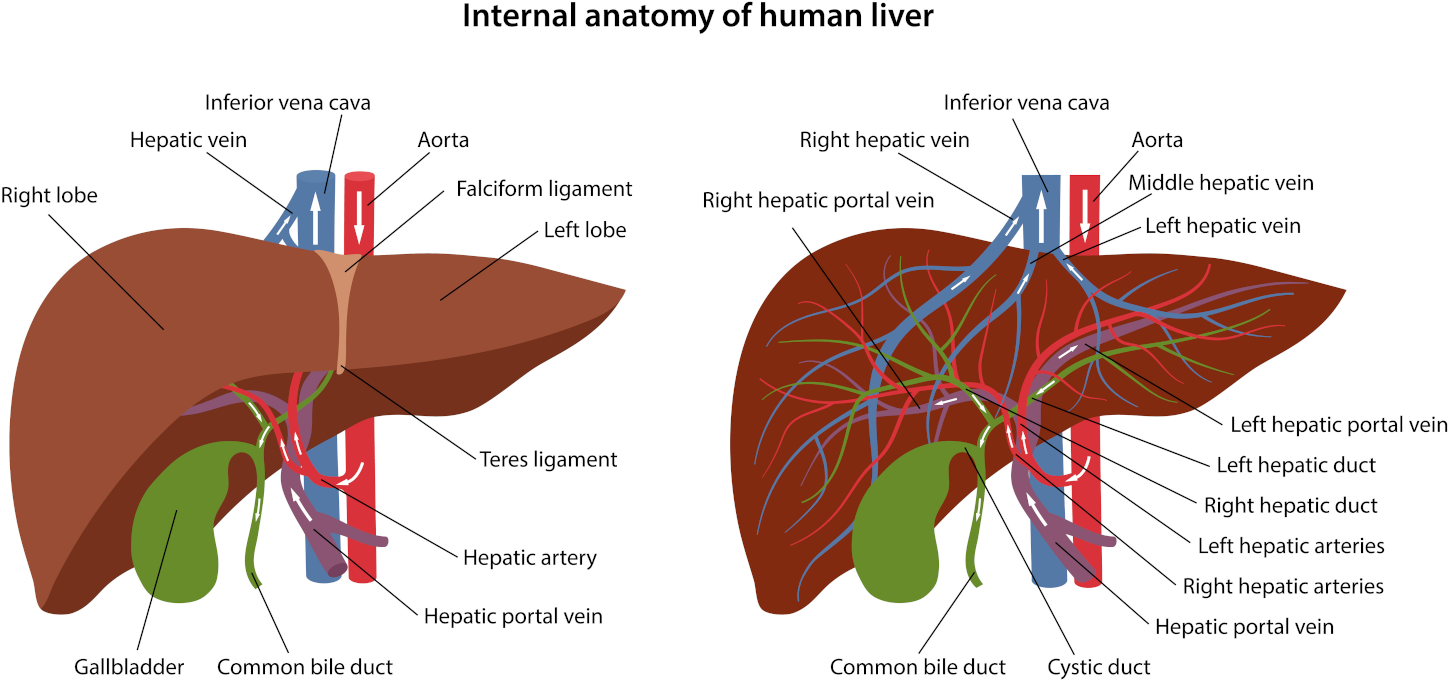
This mechanism involves the enterocyte membrane surrounding the absorbed substance to form a vesicle that plunges into the cytoplasm. Interferon enters the bloodstream of the inferior vena cava through the system of rectal venous plexuses, which is how it penetrates the network of venous vessels in the rectum. Further, it gets directly into the large circulation circle, passing the liver, realising the systemic effect.
Colonic irrigation in our clinic in London may help maintain the intestine’s health and normalise the immune system’s functioning.

Anti-candida Mini Detox – three colonics with bicarbonate of soda
The Anti-candida mini detox involves a concentrated series of three colonics infused with bicarbonate of soda, ideally scheduled once weekly. This regimen serves as a potent initiation into a detoxifying cleansing routine, setting the pace for rejuvenation.