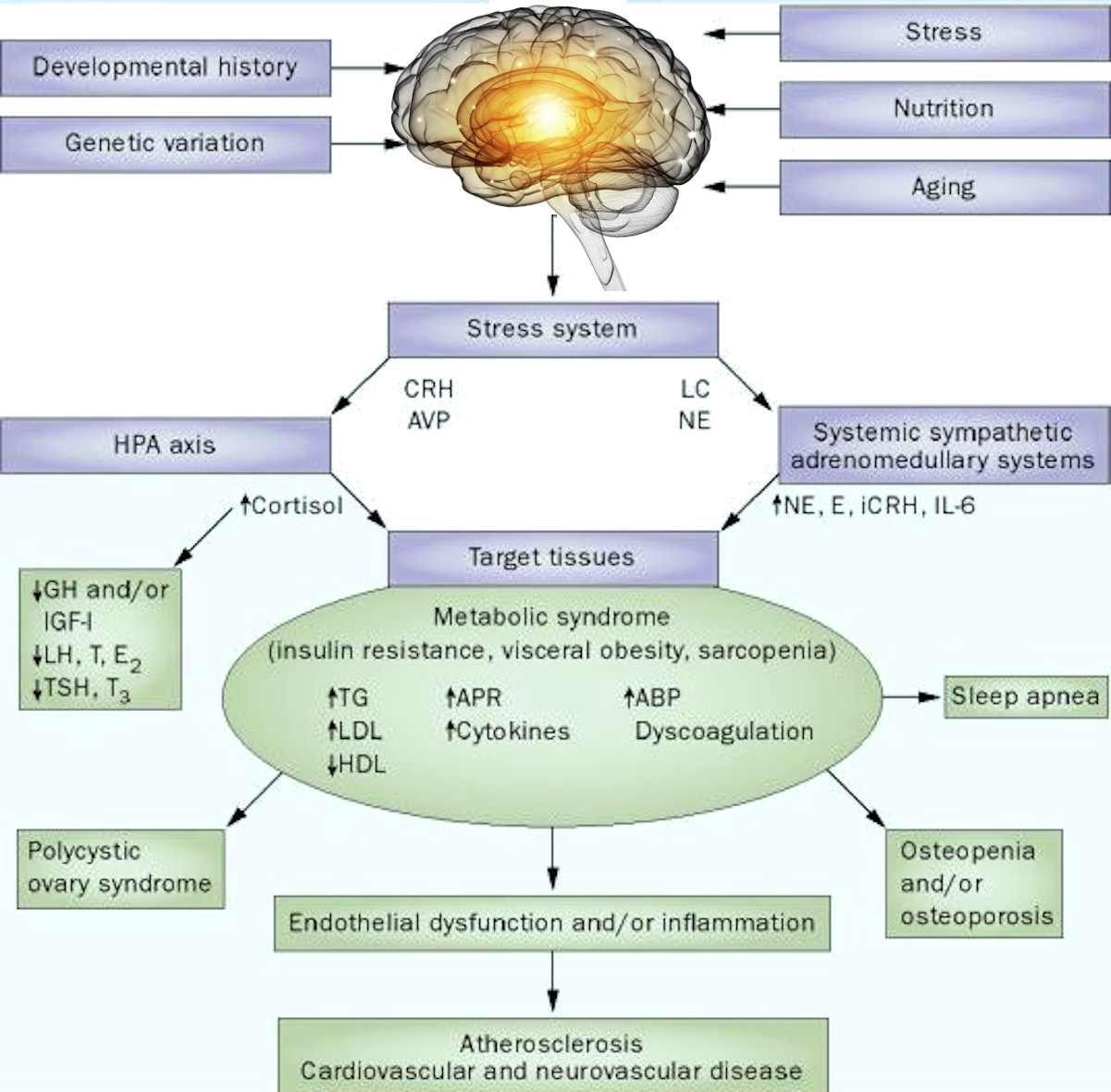
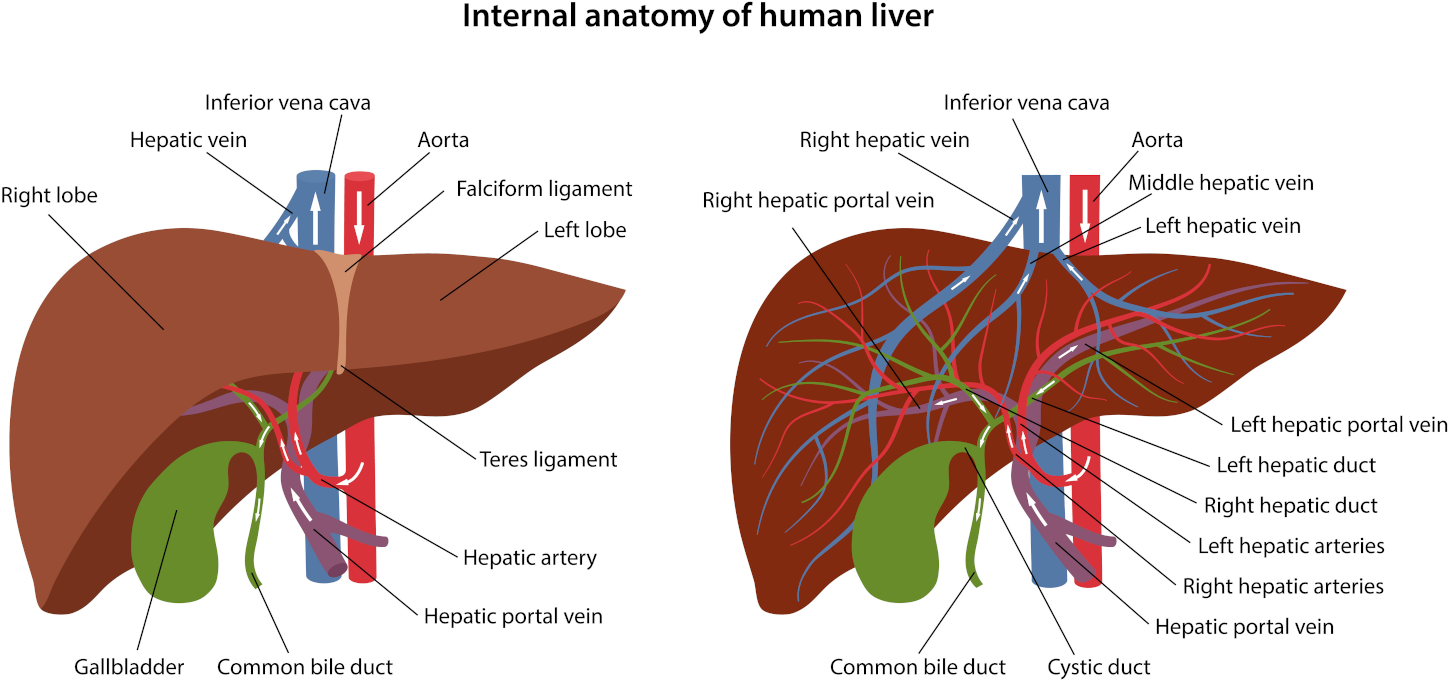
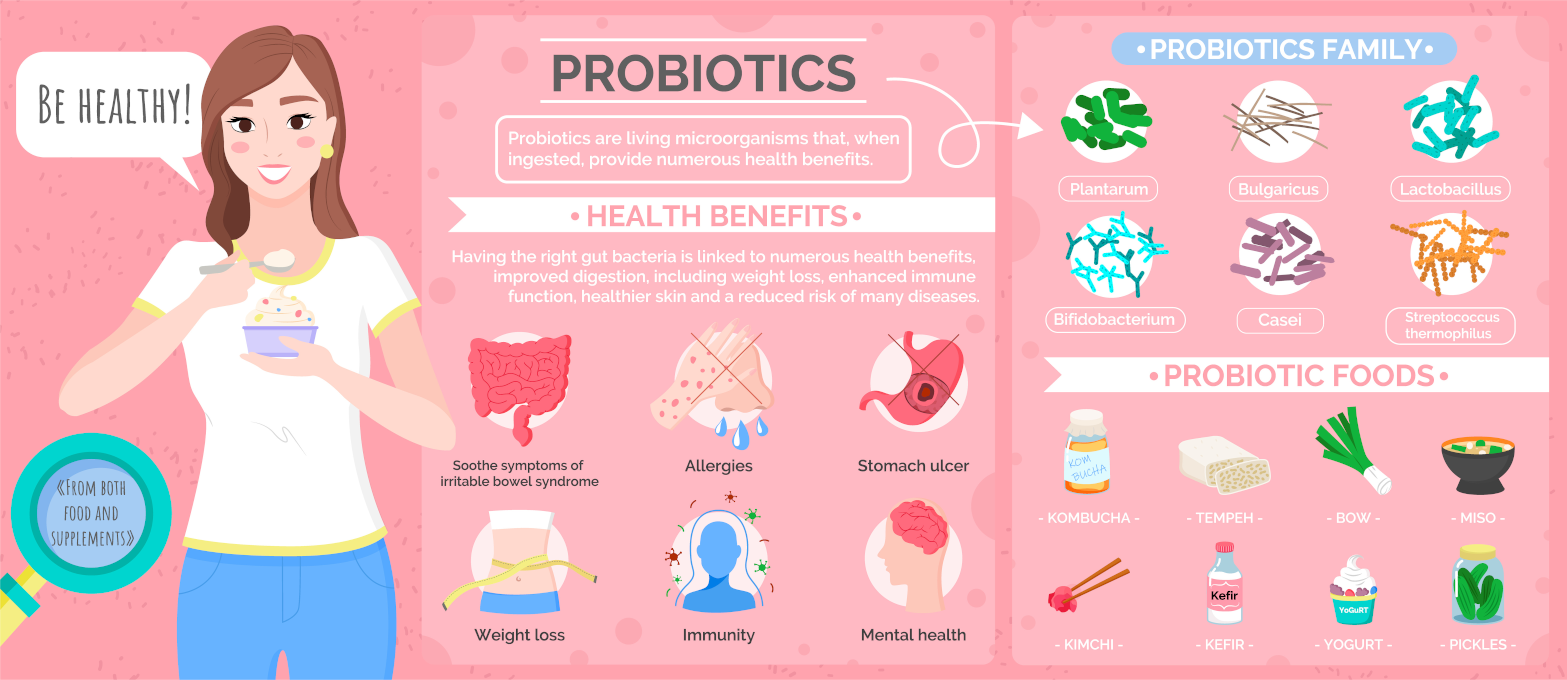
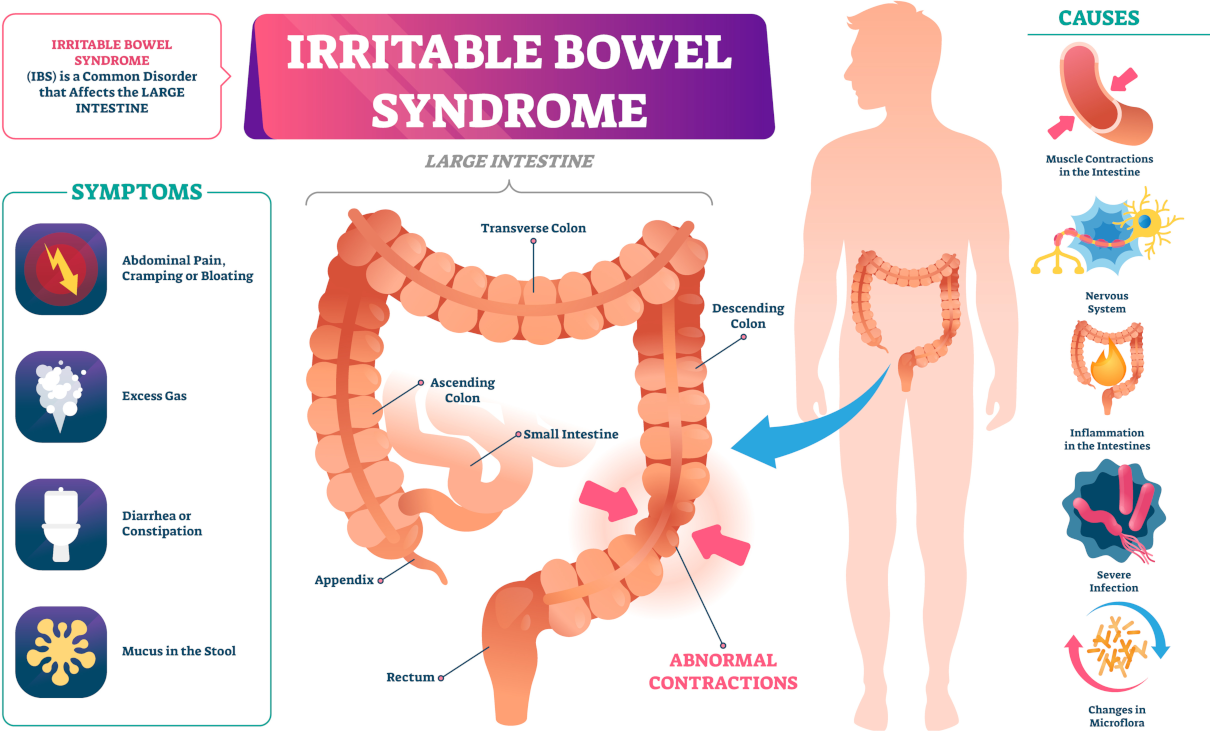
A migraine causes paroxysmal unilateral headaches accompanied by vomiting. Complex biochemical changes, such as increased serotonin and prostaglandin in the blood plasma, provoke a short spasm of the intracranial vessels followed by a continuous expansion of the extracranial arteries.
Pain
The spasm is the foundation of photopsia and other focal symptoms. The expansion of the vessels is also the direct cause of headaches. In a classical case, the migraine attack begins with a transient (sometimes ophthalmic) scotoma. As a result, patients often feel pain in the head at large.

Colonic with a liver stimulating herbal implant & bicarbonate of soda
Colon hydrotherapy with bicarbonate of soda and a herbal implant helps remove gas. It also stimulates, soothes and relaxes the liver and gallbladder. Consequently, sodium bicarbonate delivered to the colon through hydrotherapy can kill candida. Your appointment includes an initial consultation.
Symptoms
Nausea and vomiting usually accompany the pain. The attack lasted several hours. Unlike a classic, ordinary migraine, it has no visual aura. It features diffuse pain that arises in the morning and lasts several days. Rest often provokes cephalalgia (a headache on weekends). This illness variant is characteristic of women who are overweight.
Migraine attack
Cases during which the attack is accompanied by hemiplegia, aphasia, and ophthalmoplegia are known as associated migraines. The frequency and seriousness of Migraine attacks vary greatly: 50 per cent of patients have attacks less than once per week. A migraine is a widespread disease affecting 5-10 per cent of the population. The condition usually begins during adolescence or, less often, during childhood.

Mini Detox PLUS – 3 colonics, minerals, herbal & probiotic implants
The ideal pattern of colonic treatments includes three alkalising colon hydrotherapy treatments with sodium bicarbonate, one anti-parasitic implant on the first treatment, one liver and gall bladder stimulating herbal implant on the second treatment, and a high-strength probiotic implant on the third colonic.