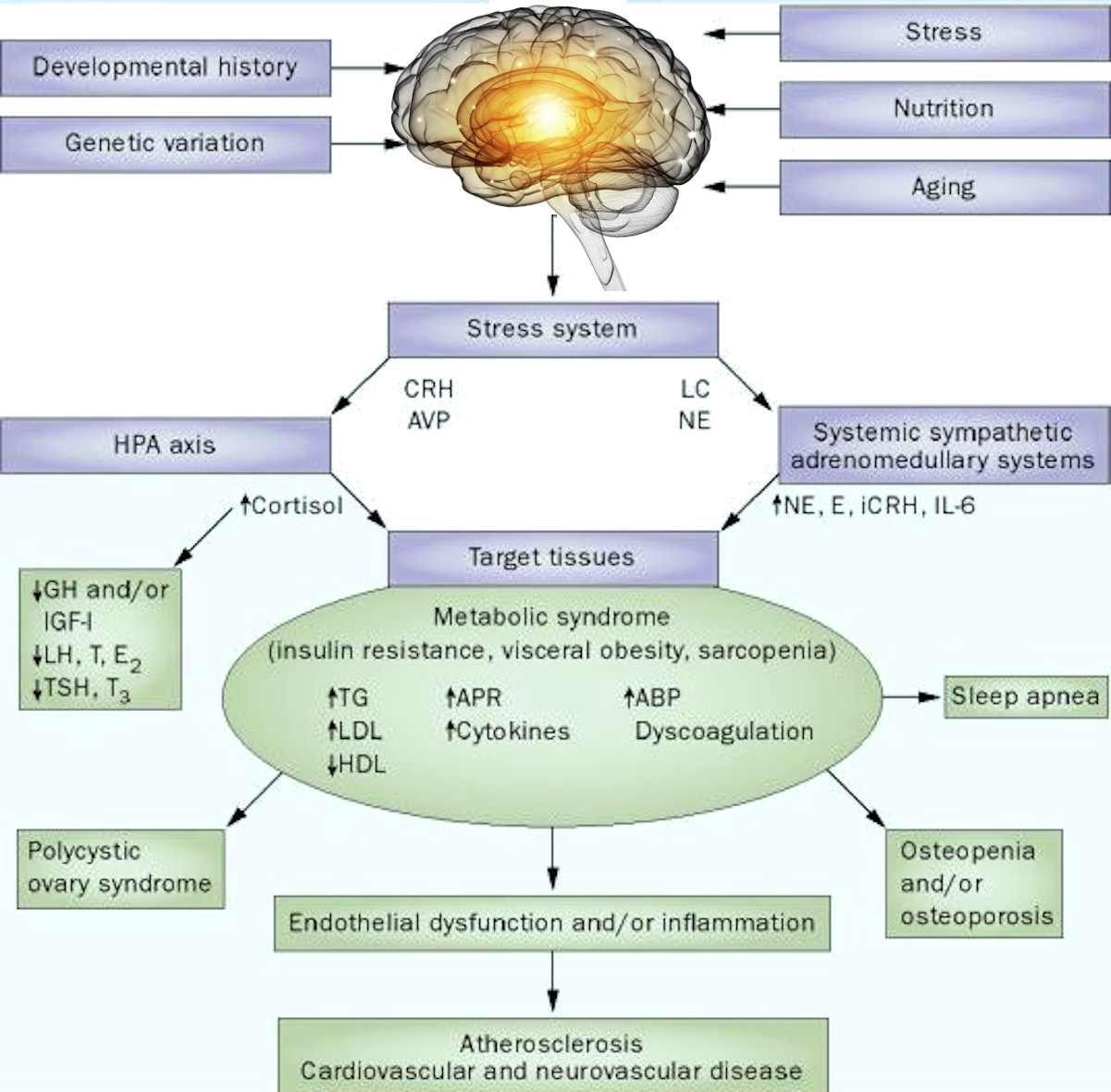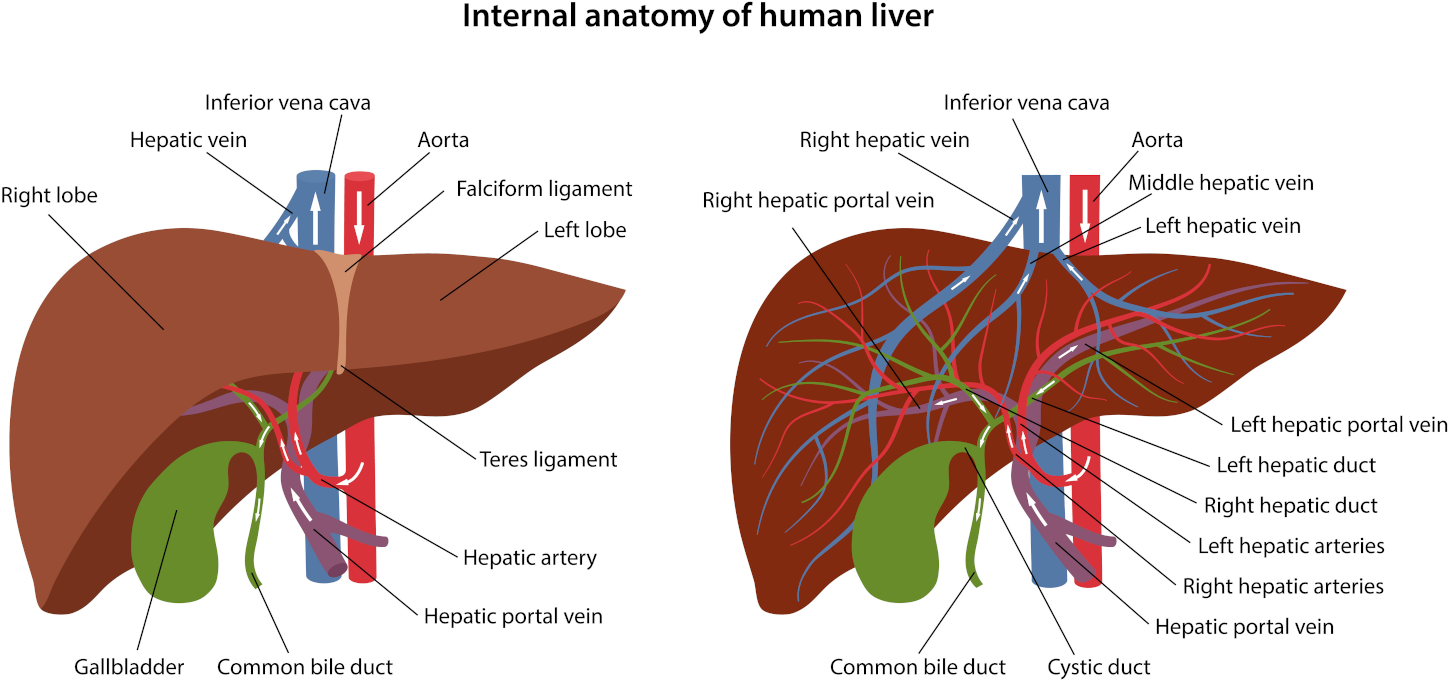
In previous articles, we discussed the liver and its various functions. Here, we will focus on the liver’s defensive role and hepatic malfunctions attributed to intestinal toxaemia. We’ll also look at the subsequent infection of other organs due to liver disability.
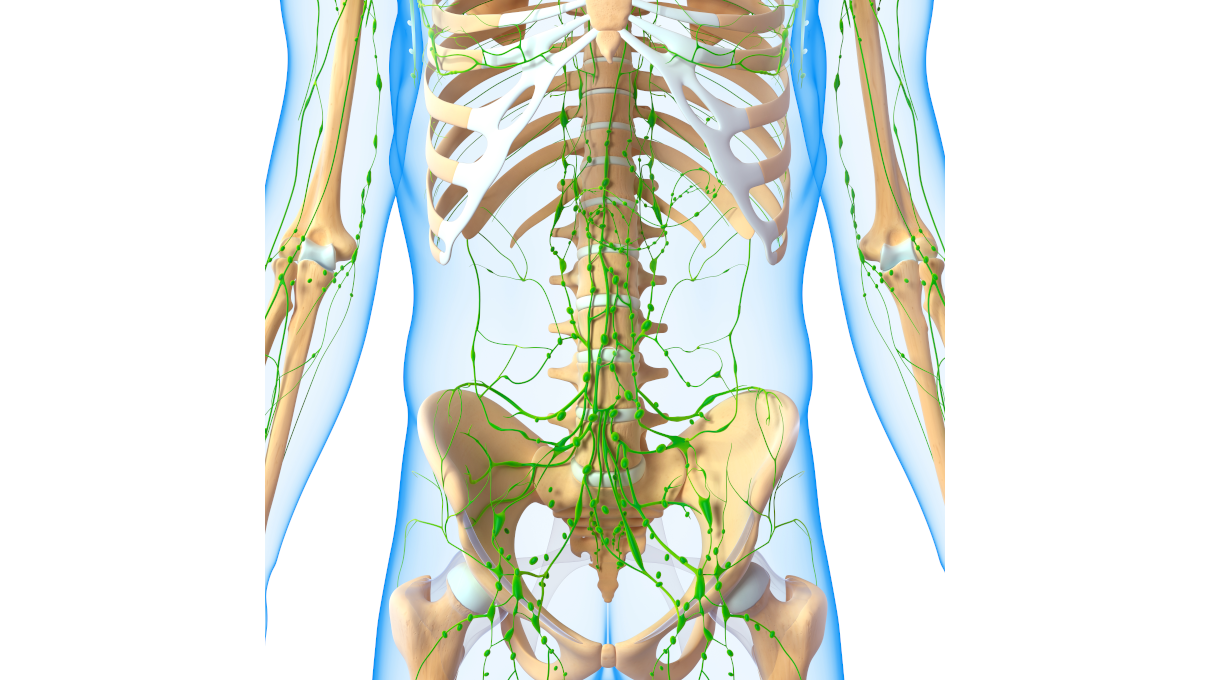
The first line of defence is naturally the mucosal lining of the alimentary tract. If bacteria or toxins penetrate the mucosal layer, they can enter the lymphatic system. Temporary increases in the portal vein’s toxic load occur during stasis, dietary insufficiencies and the flu.
Colon therapy
Any prolongation of this state will damage the detoxifying and bacteriolytic function of the liver. It’s impossible to overlook the importance of this function once we realize the strategic position of the liver concerning the circulatory system. All the “toxic” blood enters the liver for cleansing before it flows to the rest of the body. At this point, Wiltsie states that anything will cleanse the colon of bacteria and toxic material. It should also be beneficial to relieve the liver of some of its duties. He suggests that colon therapy would be advisable for liver and biliary malfunctions.

Mini Detox PLUS – 3 colonics, minerals, herbal & probiotic implants
The ideal pattern of colonic treatments includes three alkalising colon hydrotherapy treatments with sodium bicarbonate, one anti-parasitic implant on the first treatment, one liver and gall bladder stimulating herbal implant on the second treatment, and a high-strength probiotic implant on the third colonic.
Effective removal by the lymphatic system.
A competent liver forms a significant barrier between intestinal toxins and general circulation. It could lead to hepatic malfunction, allowing intestinal toxins and bacteria to be unscathed through the liver
Medical scientists thought that biliary function was independent of liver disease. Now, some physicians regard it as a secondary infection of the liver. Lymph channels common to the bladder and the liver may be another source of disease transmission. It is a liver disorder of one type or another. In other words, it stresses that we’ll most likely find the other two if we detect one of three conditions.
Remaining front
Let’s look at the liver, which cannot handle toxins from the intestine, and other focal infections, including the products of necrosis of its cells, the kidney. Unfortunately, the kidney did not evolve to reduce the number of toxins entering the
The remaining front in the second line of

Food intolerance test of 208 ingredients
This is our most comprehensive food and drink test. It analyses your client’s IgG antibody reactions to 208 food and drink ingredients. This test will highlight their food triggers and help you formulate an IgG-guided elimination diet together.