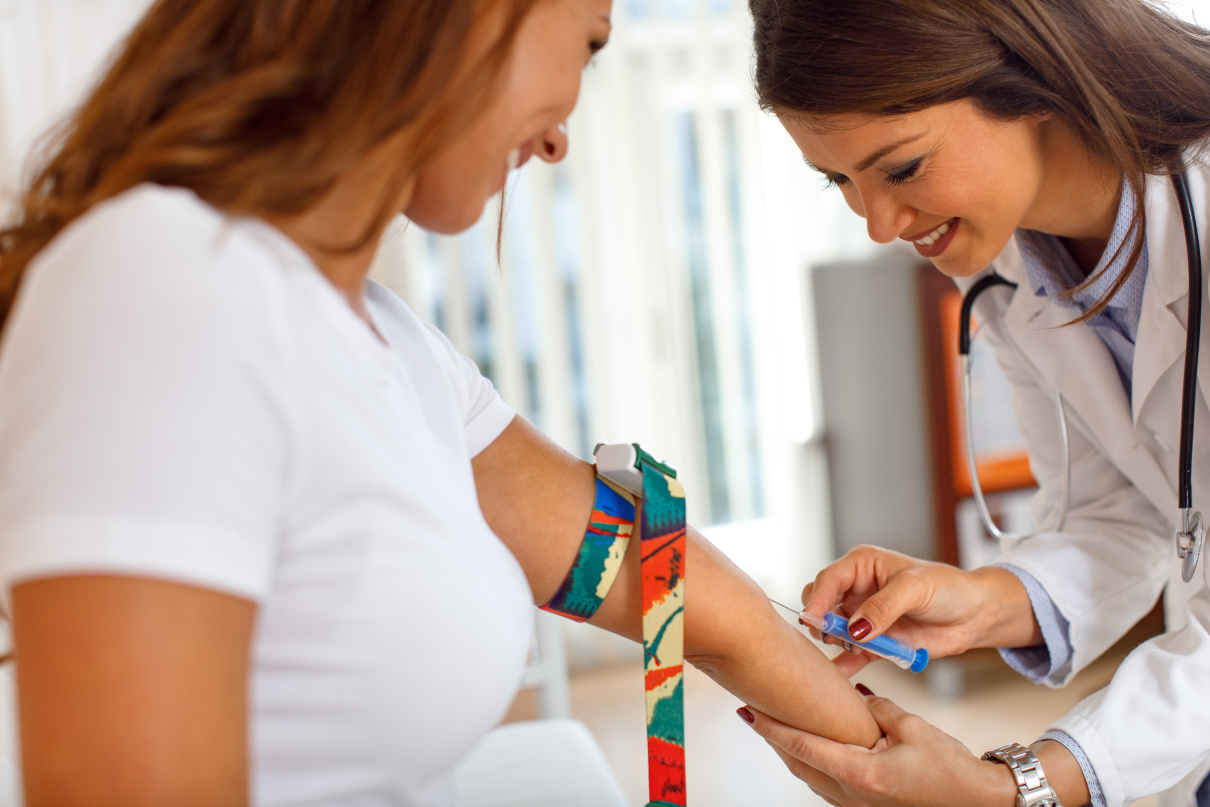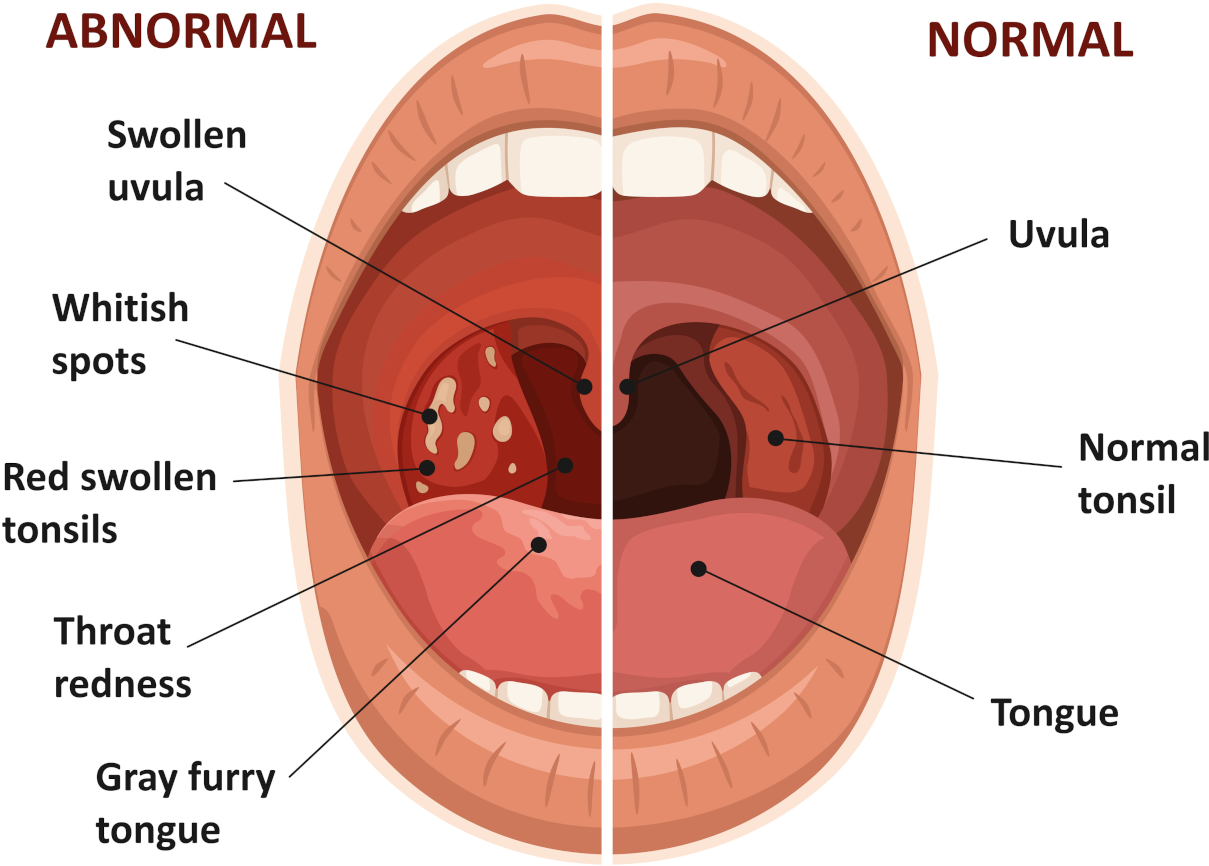
Acute tonsillitis is a widespread, severe infectious disease that primarily affects the palatine tonsils. The inflammatory process may also involve other areas of the lymphadenoid pharynx and larynx, including the lingual, laryngeal, and nasopharyngeal tonsils. The infection process can be exogenous (more often) or endogenous (autoinfection).
Infection and tonsillitis
Tonsillitis can be either airborne or alimentary in transmission. Endogenous infection involves the oral cavity or pharynx (chronic inflammation of the palatine tonsils, caries, etc.). Suppurative diseases of the nose and sinus may prompt this kind of infection. Moreover, staphylococci, streptococci (especially haemolytic), and pneumococci usually promote the condition.
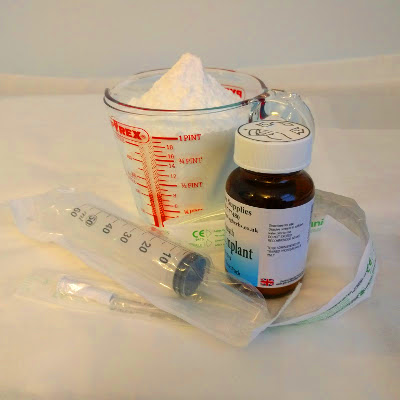
Probiotic implant and alkalising colonic with bicarbonate of soda
Alkalising colonic irrigation with bicarbonate of soda and high strength probiotic implants and comprehensive consultation is available at Parkland Natural Health Clinic.
Factors
There is certainly evidence that tonsillitis may promote quinsy featuring viral aetiology. Among precipitating factors are local and general hypothermia and decreased organism reactivity. Quinsy usually affects children of both school and pre-school age and adults up to thirty-five to forty years of age, especially in autumn and spring. Patients typically run a high temperature, suffer from malaise and feel pain when swallowing. People with tonsillitis also complain of joint pain, headaches, periodic fevers, etc.
Colonic irrigation may ease symptoms and speed up recovery. Moreover, regular colonics with probiotic implants can improve the immune system and make people more resistant to the abovementioned infections.

Anti-candida Mini Detox – three colonics with bicarbonate of soda
The Anti-candida mini detox involves a concentrated series of three colonics infused with bicarbonate of soda, ideally scheduled once weekly. This regimen serves as a potent initiation into a detoxifying cleansing routine, setting the pace for rejuvenation.