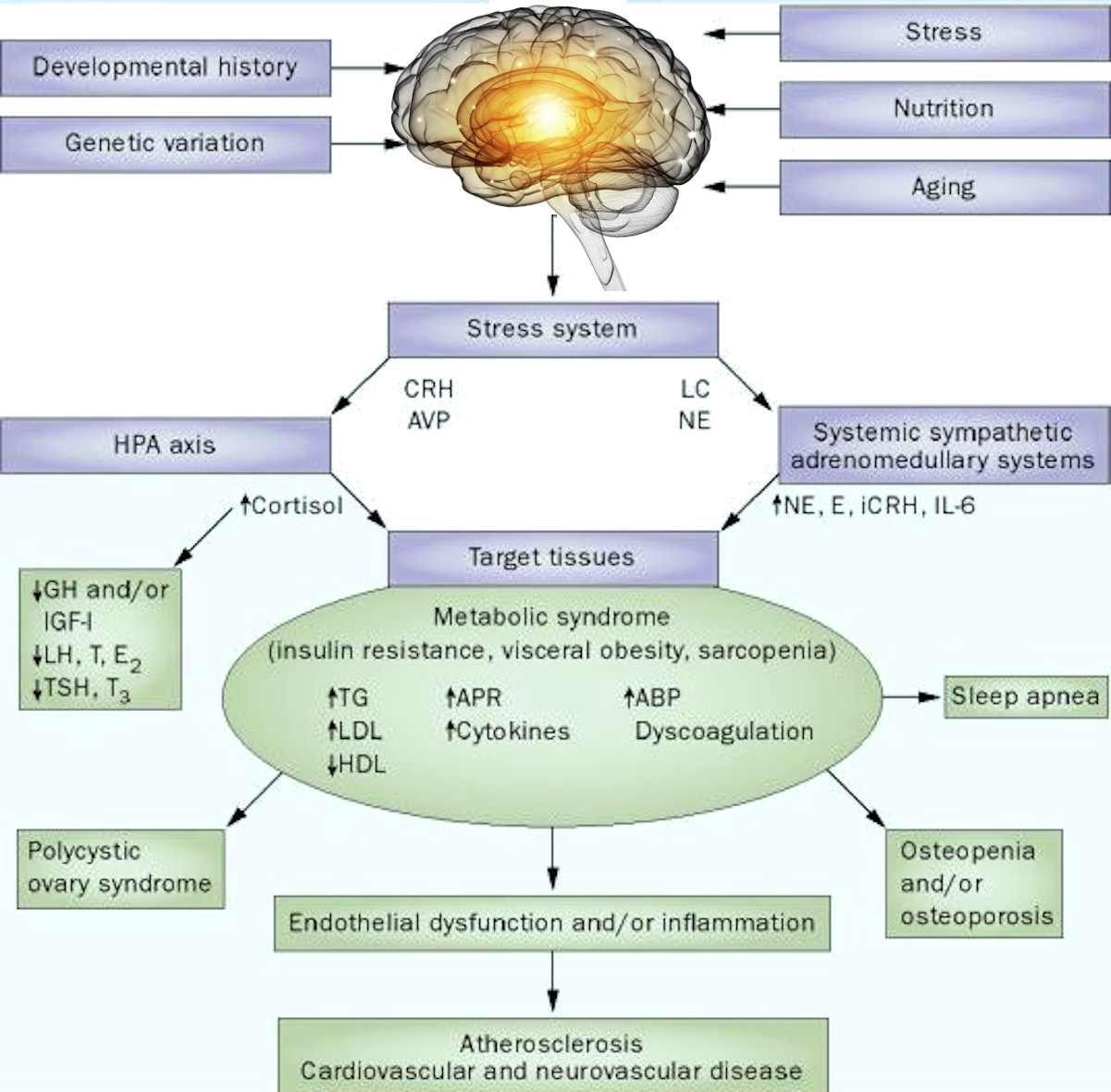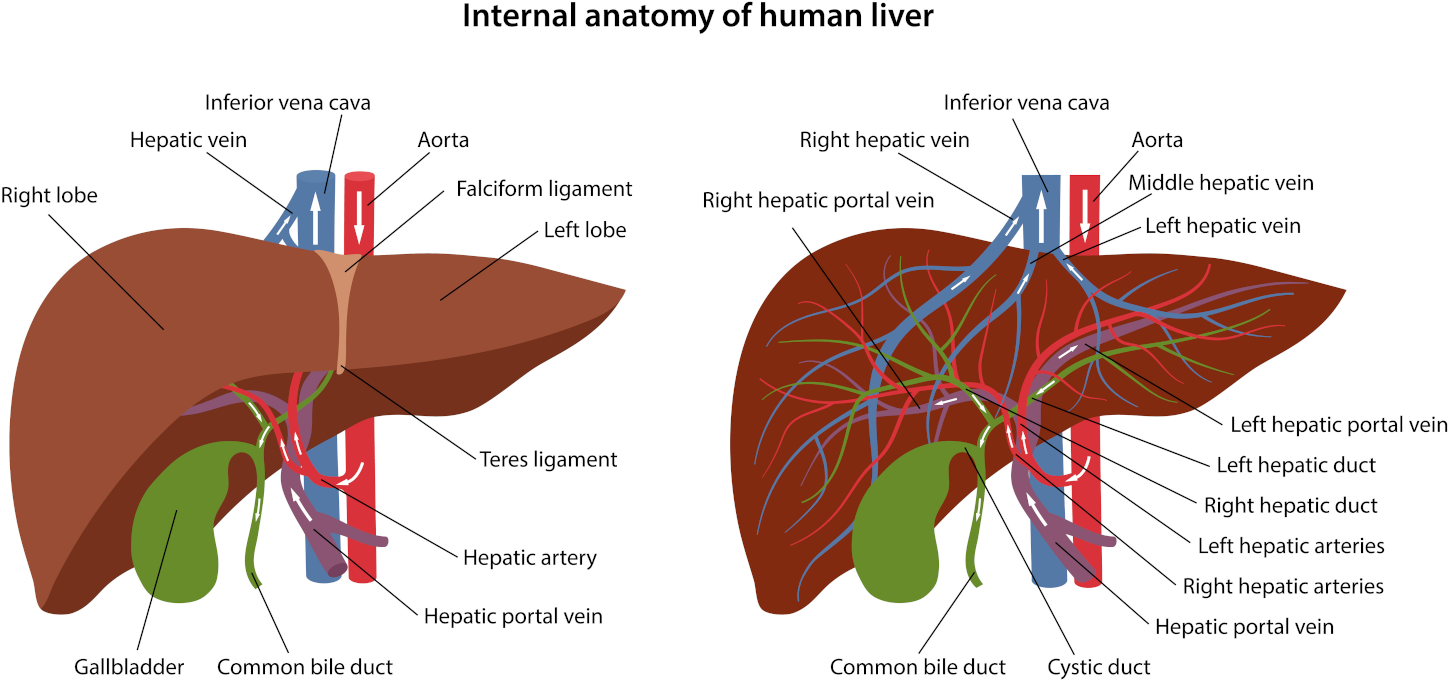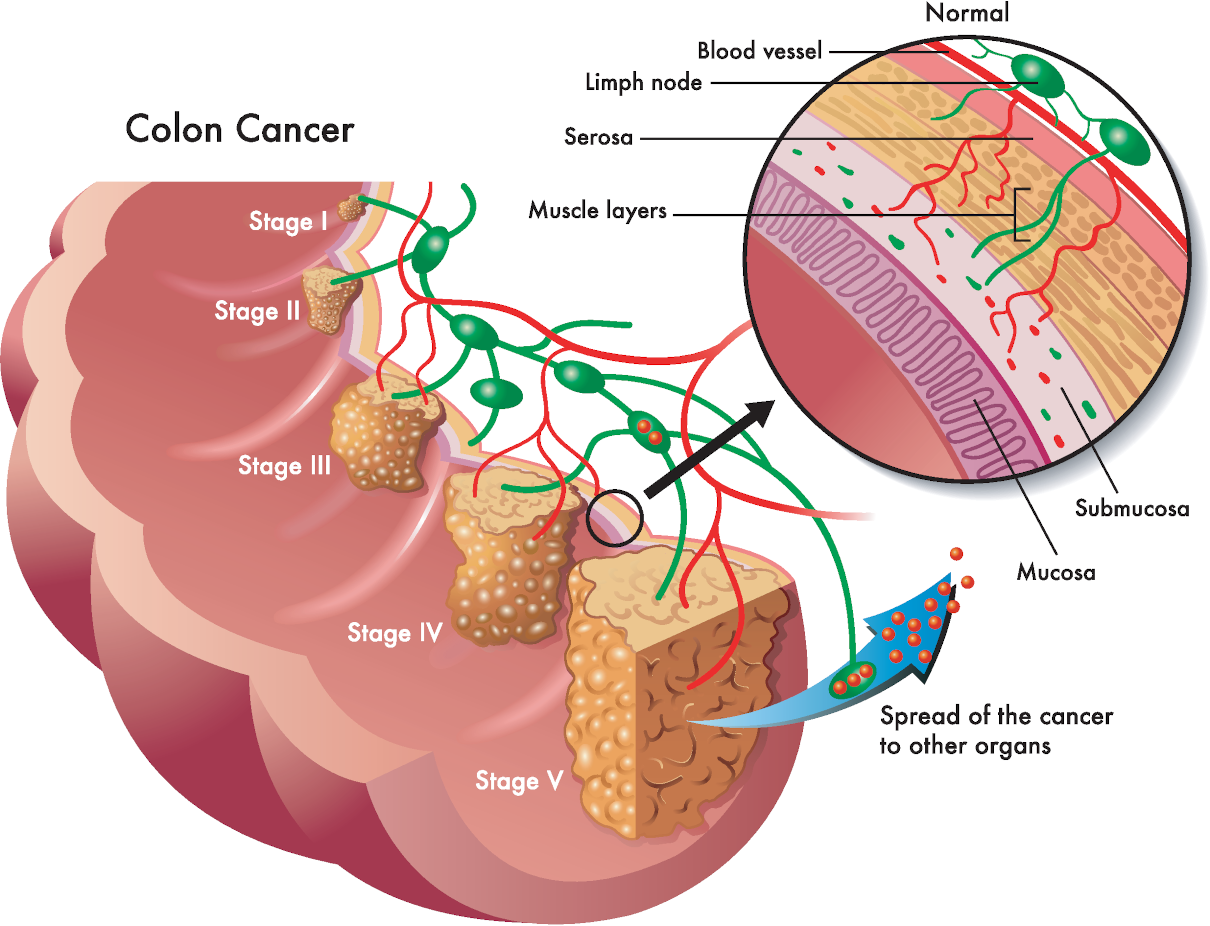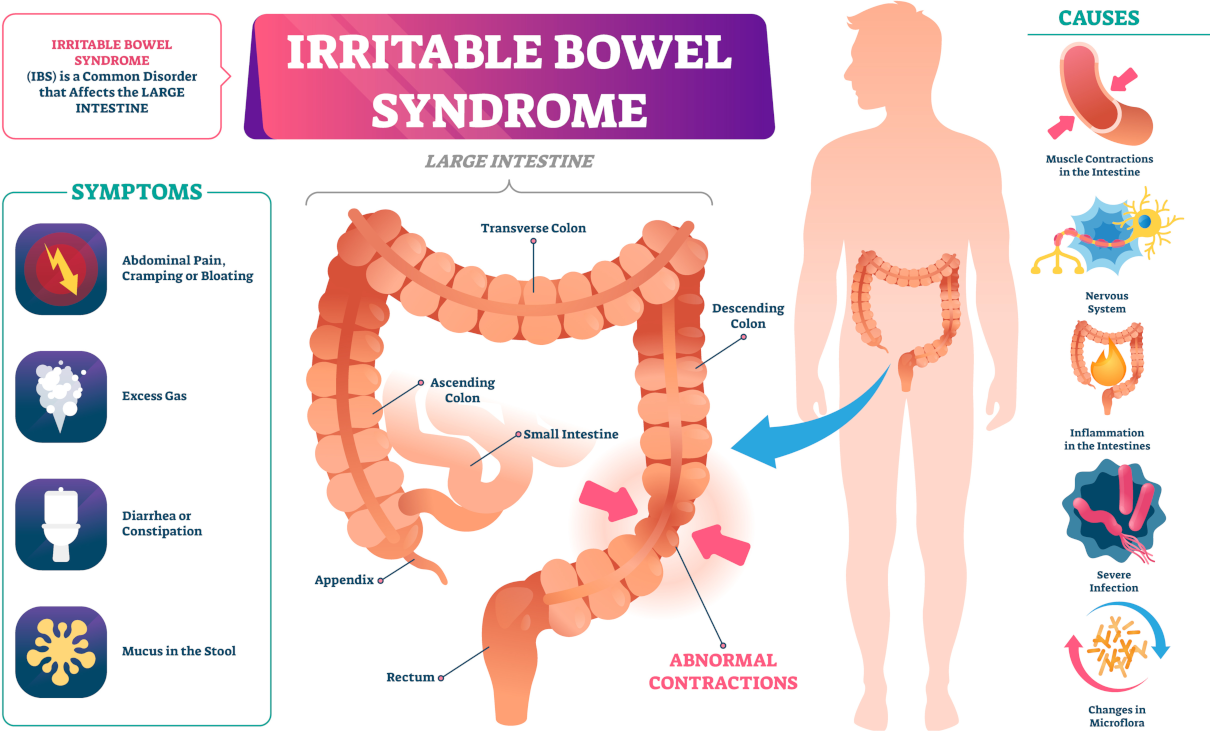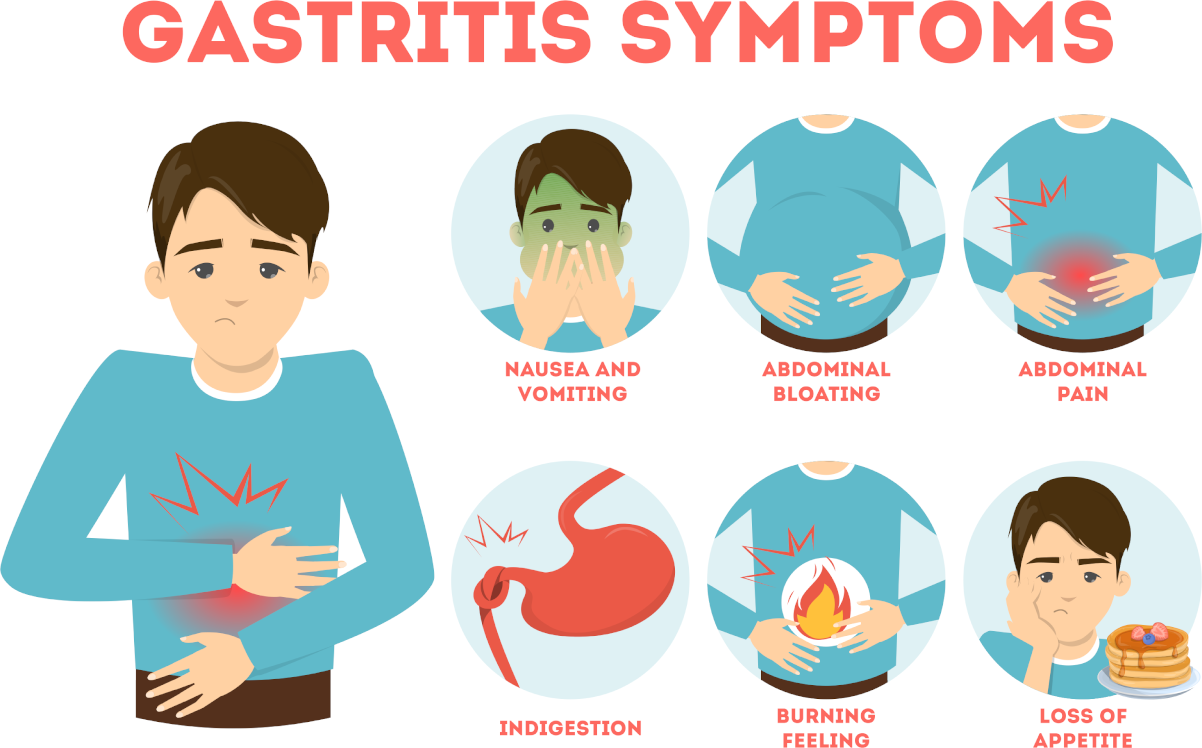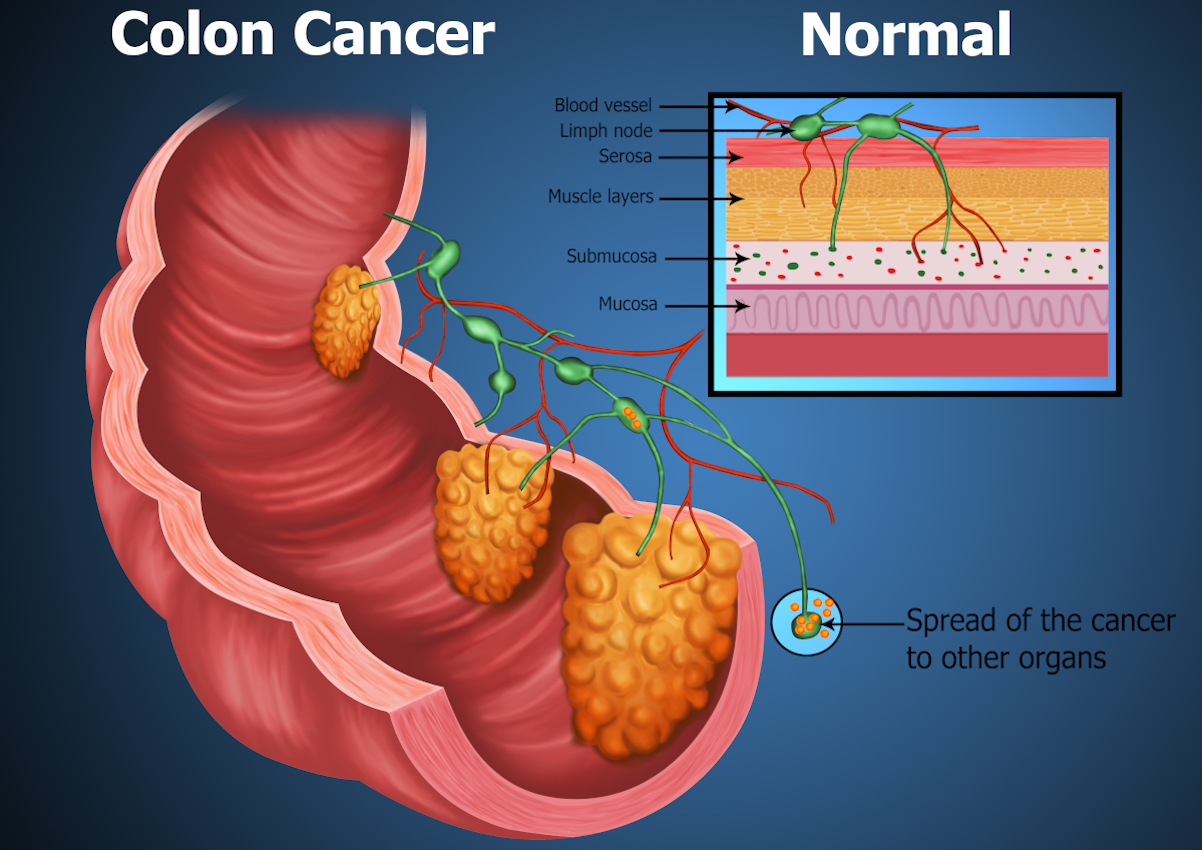
/Intestinal obstruction in case of oncology./ In 60 to 70% of cases, a tumour or its metastases bowel cause obstruction in cancer. Also, 20 to 30% occur due to gastrointestinal tract diseases. And, in 10 to 20%, a metachronous tumour causes obstruction, which is removable surgically as typical. Such malignant neoplasms often cause intestinal blockages such as ovarian cancer and gastrointestinal tract tumours.
Pathogenesis of intestinal obstruction in case of oncology:
- compression of the intestine from the outside;
- obturation of the intestine from the inside;
- paralytic intestinal obstruction due to local or diffuse disruption of intestinal motility due to germination of the nerve plexus by a tumour;
- invagination of the intestine in some tumours, usually with melanoma;
- pseudo-intestinal obstruction.

Anti-candida Mini Detox – three colonics with bicarbonate of soda
The Anti-candida mini detox involves a concentrated series of three colonics infused with bicarbonate of soda, ideally scheduled once weekly. This regimen serves as a potent initiation into a detoxifying cleansing routine, setting the pace for rejuvenation.
Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis:
- Pink periwinkle alkaloids cause constipation. Reduced bowel tone and paralytic intestinal obstruction, especially in the elderly, can lead to high faecal blockages and mechanical intestinal obstruction. It is easier to prevent faecal blockage than to heal.
- Radiation enteritis in radiography and CT-scan of the abdomen manifests by smoothing the mucous membrane, ulcers, strictures, rigidity, adhesions expansion of the intestine and thickening of its wall.
- Diverticulitis is the cause of pronounced strictures of the distal colon. Those are radiographically indistinguishable from exophytic cancer, usually without metastases.
- Other non-tumour causes of intestinal obstruction include intestinal adhesions, intestinal hernias, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, intestinal volvulus, spontaneous invagination of the intestines, acute pancreatitis and intestinal infarction.

Boyzone waxing including back, sac and crack
Modern hair removal methods allow a man to eliminate unwanted hairiness in intimate areas for up to three weeks. Our specialists have all the necessary skills and perform bikini waxing for men quickly, efficiently and safely in our London clinic.
Therapy in cases of Intestinal obstruction in case of oncology
Treatment of intestinal obstruction caused by a tumour:
- Intestinal decompression.
- Stent installation.
- Surgery. A malignant tumour is not always a contraindication to surgery. Approximately 75% of patients, after surgery, restored normal bowel function. Intestinal obstruction no longer recurs in 45% of patients. However, about 25% of patients do not improve their condition after surgery.
Operation
The patient’s condition may not improve in 4 to 5 days after decompression of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, the operation is advisable for intestinal obstruction in the case of oncology. I’m sure colonic hydrotherapy may also help cleanse the intestines of waste and toxins.

One colonic irrigation session including consultation
Colon irrigation and comprehensive consultation with a professional colon hydrotherapist registered with RICTAT and ARCH at the Parkland Clinic in Holborn. We use a closed system only—London’s best colonic hydrotherapy deal.