What is the proper way of correction of intestinal microflora?
Comments 0 7th September 2018 Blog, General
The decisive role of correcting intestinal microflora of the human intestine is excellent. By providing antigenic irritation of the mucous membrane, the intestinal autoflora stimulates the maturation of mechanisms of general as well as local immunity.
Flora generates lactic, acetic, formic, propionic, and butyric acids during its vital activity. So, they promote acidification of the chyme. They also prevent the propagation of pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria in the intestine. Intestinal autoflora synthesises antibiotic substances such as colicin, lactolin, streptocid, nisin and lysozyme. Besides, they have a bactericidal or bacteriostatic effect on pathogens.

Colonic with a liver stimulating herbal implant & bicarbonate of soda
Colon hydrotherapy with bicarbonate of soda and a herbal implant helps remove gas. It also stimulates, soothes and relaxes the liver and gallbladder. Consequently, sodium bicarbonate delivered to the colon through hydrotherapy can kill candida. Your appointment includes initial consultation.
Antibiotics and microflora
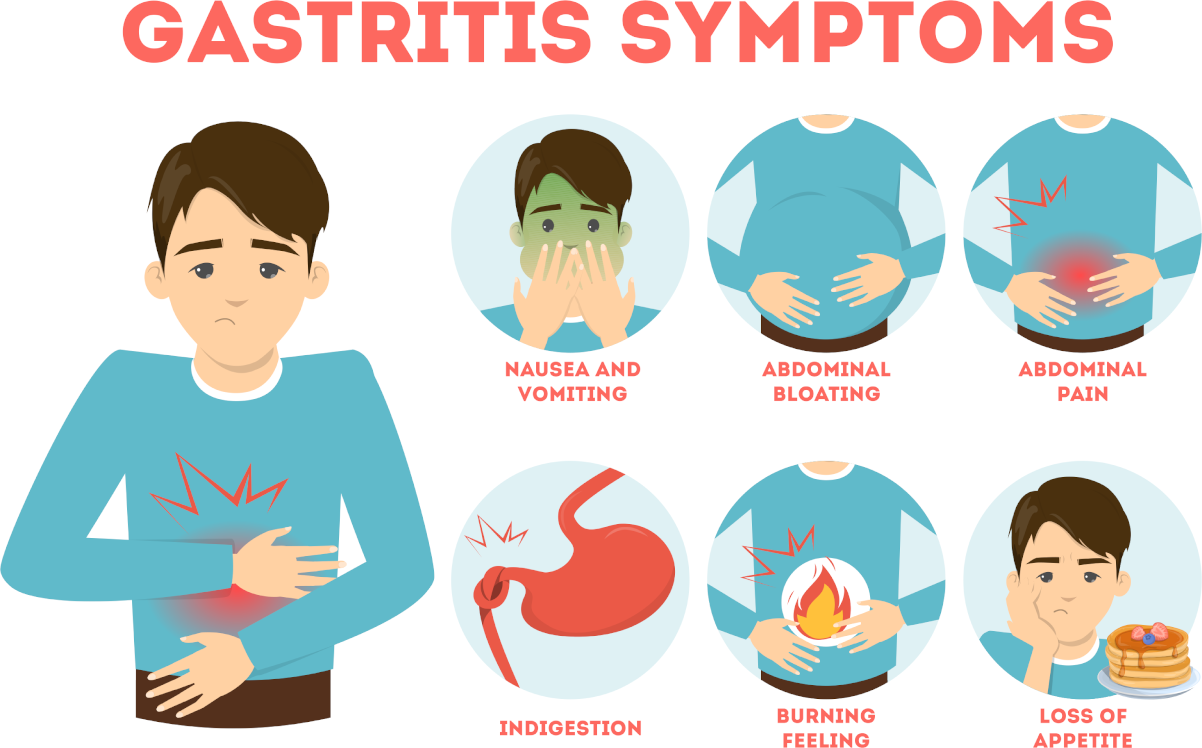
Nevertheless, the microflora composition in the intestine biofilm can vary under various factors. If these factors, affecting the fixation directly or indirectly, survival and functioning of healthy intestinal microflora exceed the body’s defence mechanisms, they provoke the development of intestinal dysbiosis. So, to restore it, proper correction of intestinal microflora is necessary.
Thus, antibiotics have the most pronounced adverse effect on healthy intestinal microflora. Furthermore, microbiological disorders occur in prescription adsorbing, laxatives, expectorants, and choleretic drugs. These groups of medicines, when administered internally, change the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, disrupting the formation of mucus and contributing to the development of an imbalance in the healthy microflora. In newborns and infants, a violation of the intestinal microbiocenosis may be due to the aggravated course of pregnancy, childbirth, and infanticide.

Food intolerance test of 208 ingredients
This one is our most comprehensive food and drink test. The test analyses your client’s IgG antibody reactions to 208 food and drink ingredients. This test will highlight their food triggers and help you formulate an IgG-guided elimination diet together.
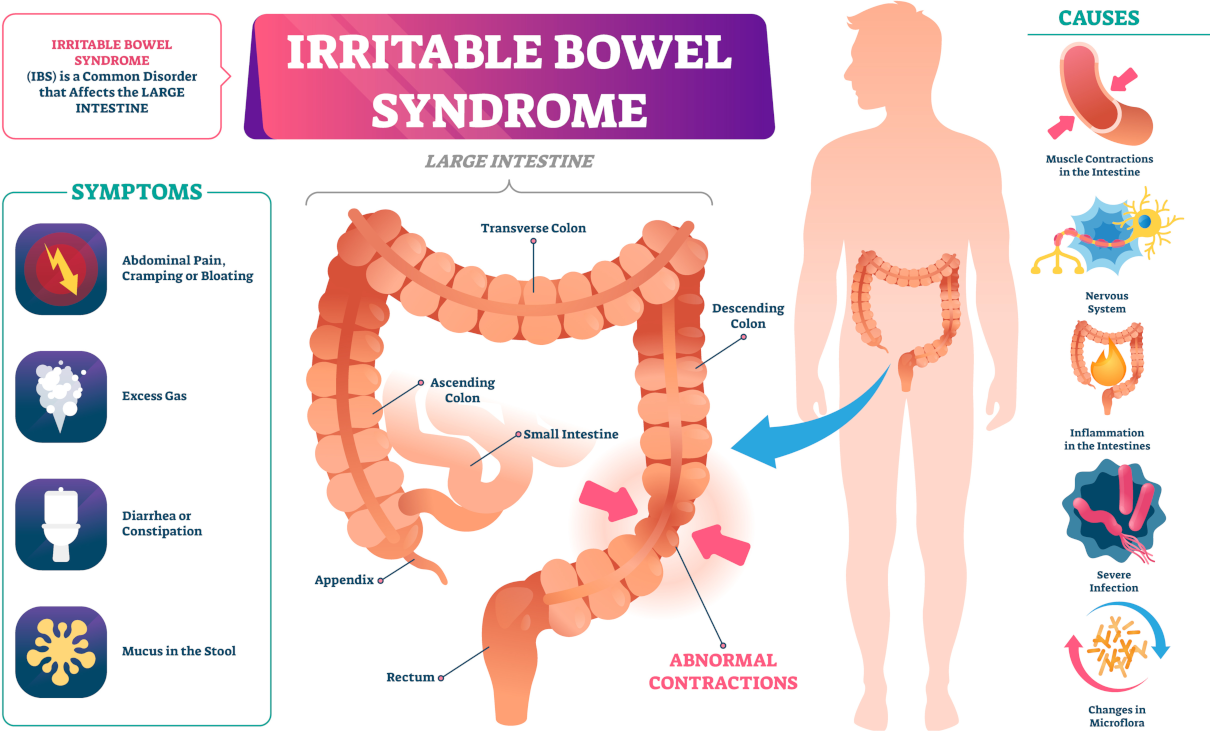
Correction of intestinal microflora and symptoms of pathology
The spectrum of clinical syndromes and diseases associated with intestinal dysbiosis is now relatively broad. Besides, it tends to increase. Here are some of them:
- diarrhoea,
- constipation,
- colitis,
- malabsorption syndrome,
- hypertension,
- raised cholesterol levels in the blood,
- urolithic and cholelithiasis,
- atopic dermatitis,
- bronchial asthma,
- liver pathology,
- Malignant neoplasms.
Correction
Also, the correction of intestinal microflora sets the main tasks for itself:
- elimination of excess bacterial contamination of the small intestine;
- restoration of healthy microflora of the small intestine;
- improvement of intestinal digestion and absorption;
- restoration of impaired intestinal motility;
- The normalisation of the gastrointestinal part of the immune system.
Full leg + Hollywood or Brazilian + underarm + full arm waxing
This treatment will eliminate unwanted hair, and the effect will last three to four weeks. A qualified therapist carries out Epilation. This treatment lasts ninety minutes.