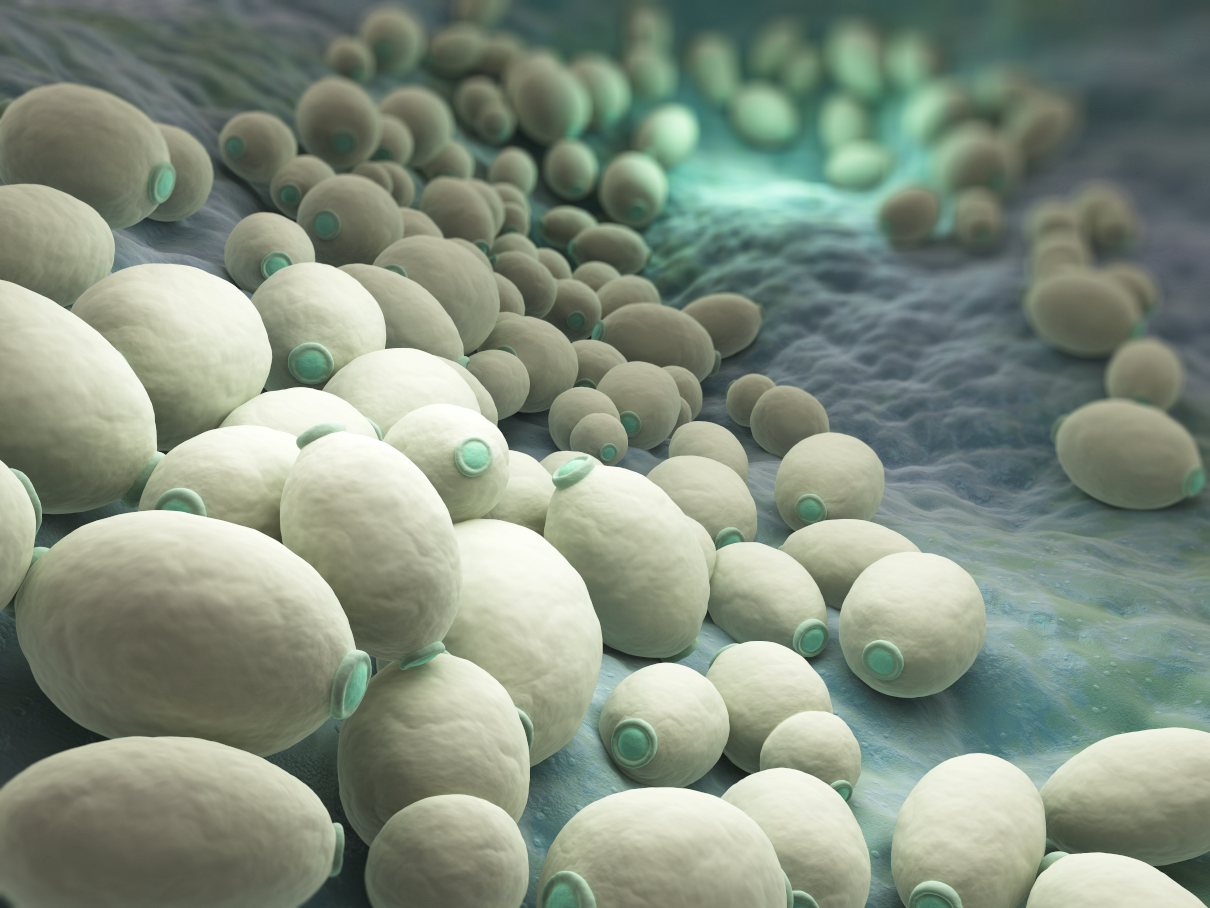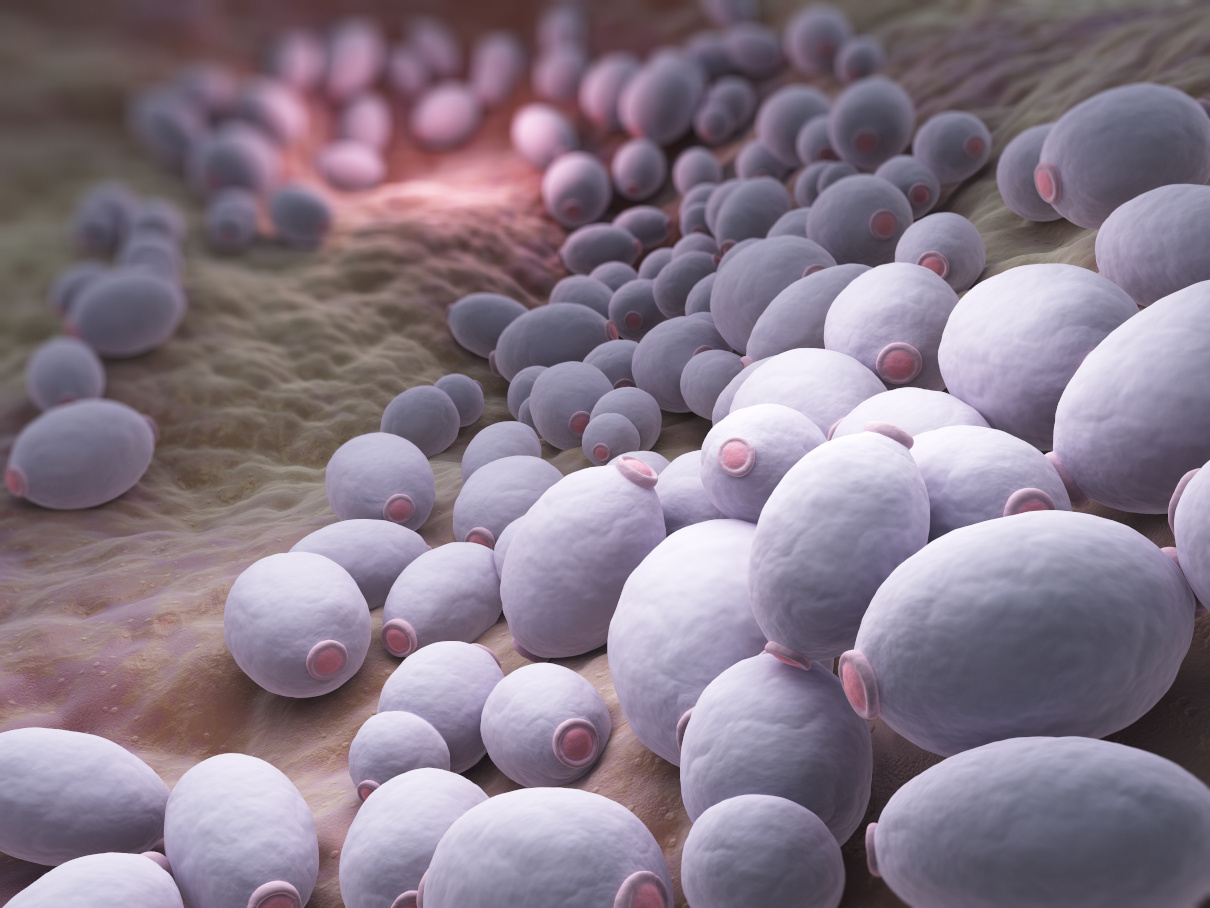
Candida albicans is a constituent of the human organism’s microscopic flora. In the early 20s, candidiasis occurred relatively rarely, but with antibiotics in the 40s, it became far more frequent, and the number of cases steadily increased. Now, Candida is the most widespread pathogen of opportunistic mycosis. It may also cause mucous and cutaneous lesions and systemic diseases. Generally, candidiasis has an endogenic origin. It results from dysmetabolic disorders and immune system dysfunctions.
There are over 150 species of mycosis pathogens. C. Albicans cause over 90% of lesions. Any dysfunctions of immunocompetent cells or normal microbial cenosis initiate the disease. Babies are infected when passing through the parturient canal or during breastfeeding. Urogenital candidiasis is transmitted sexually. Cutaneous injuries, increased perspiration and maceration promote candidiasis development.
Microflora
The microbial cenosis disturbance causes excessive growth of Candida Albicans due to the disproportional use of broad-spectrum antibiotics or a change in the surrounding microflora composition. Metabolic or hormonal disorders such as diabetes mellitus, pregnancy and peroral contraceptive administration also promote candidiasis. Besides, immunodeficiency or immunodepressants (such as glucocorticoids) can cause speedy forms of chronic candidiasis. Further, it will affect the skin or mucosa.

Anti-candida Mini Detox – three colonics with bicarbonate of soda
The Anti-candida mini detox involves a concentrated series of three colonics infused with bicarbonate of soda, ideally scheduled once weekly. This regimen serves as a potent initiation into a detoxifying cleansing routine, setting the pace for rejuvenation.
Result treatment for Candida Albicans
Surface candidiasis develops where high temperatures and dampness are present (for example, in skin folds). It also emerges because of cutaneous maceration resulting from repeated contact with water. The manifestations of candidiasis intertrigo are an erythematous rash or a vesicular-pustular rash with signs of maceration (generally around skin folds in children), which leads to erosion. Besides, mucocutaneous candidiasis often emerges in a cavity or the vagina.
The disease develops with metabolic disorders in the background or with abnormal microbial cenosis. Candidatiasis of the mouth (mycotic stomatitis) is typically treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics. It can also indicate immunodeficiency conditions. The characteristic manifestations are white and yellowish agmina on the mucosal surface. The lesions commonly combine with diffuse erythema and extremely dry mucosa.
Platelets Rich Plasma Injections – one session
Platelet-rich plasma injections are widely used in aesthetic medicine to rejuvenate and slow ageing. They use the person’s unique tissue growth factors.
Transplantation
The vulvovaginitis caused by Candida Albicans is very common in women who take perorative or intrauterine contraceptives. Those in their last trimester of pregnancy (the condition accounted for by the immunodepressive effect of factor associated with serum alpha-globulin) may experience the same. Disseminated candidiasis is a result of an invasion of pseudohyphae into parenchymatous organs. And that results in microabscesses in those organs with an occasional granulomatous inflammatory reaction. Cases without medication end up fatally.
Deep mycosis develops as a result of
- organ transplantation,
- heart surgery,
- long-term venous catheterization,
- prosthetic implantation,
- overeating,
- long-term glucocorticoid
- or immunodepressant administration.
Dissemination of surface candidiasis occurs relatively rarely. The most common are lesions of the kidneys, eyes, encephalon and heart. Multiple nidi are primarily revealed in the case of continuous contamination, for example, through a catheter.

Full belly waxing
Waxing hair removal of the back and abdomen is carried out at the highest level of professionalism in our clinic in London. If you have unwanted hairs in these areas that bother you, then there is a rapid and effective solution to this problem: hot beeswax depilation.